Key Takeaways
- Diesel is heavier and has a higher density than gasoline.
- Diesel is thicker and has a higher viscosity than gasoline.
- Gasoline floats on diesel if mixed due to lower density.
- Water sinks in diesel if present in the tank, posing contamination and corrosion risks.
- Diesel engines use compression ignition and have stronger internal parts compared to gasoline engines.
Table of Contents
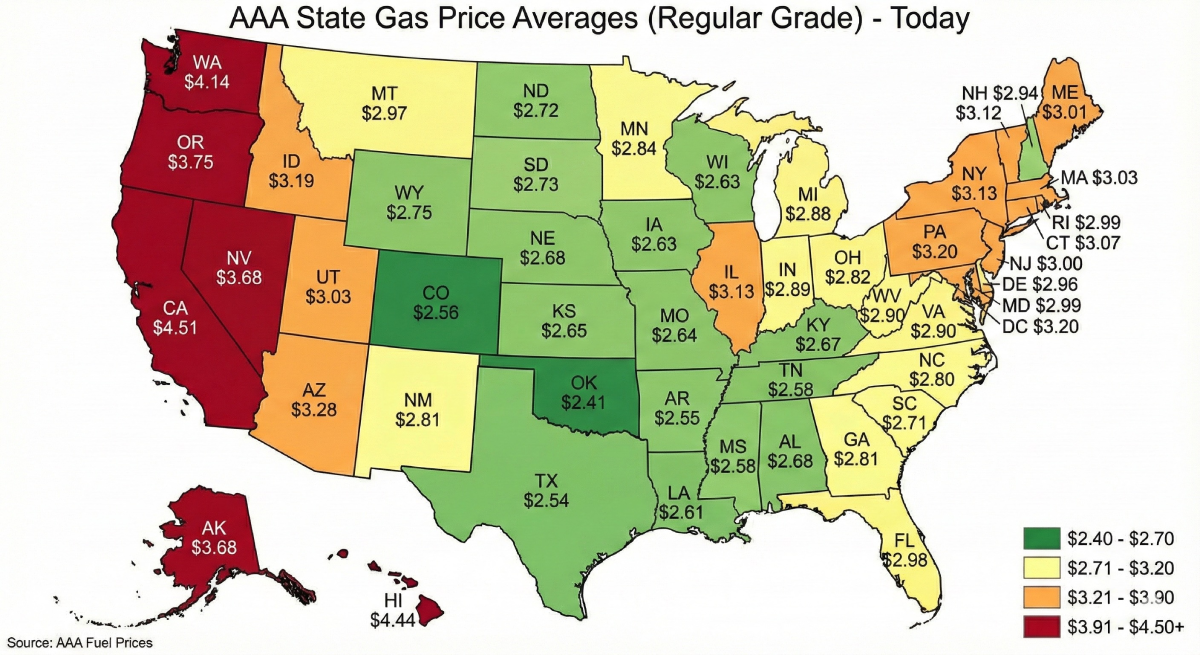
Is Diesel Heavier Than Gas?
If you’ve ever wondered if diesel is heavier than gas, the answer is generally yes. At 59F, diesel typically has a density ranging from about 1.81-1.94 lbs per liter. Gasoline, on the other hand, is lighter, with a common density of 1.56-1.69 lbs per liter. This means that a gallon of diesel weighs approximately seven lbs, while a gallon of gasoline is about 6lbs. These weight differences are important in industries like transport and shipping, where they directly impact payload limits and compliance regulations. Aviation managers and fleet planners also need to consider these factors, often adjusting loads based on temperature and density correction. For consumers comparing which is heavier diesel or gas, it’s good to know that this ranking usually holds true in most typical climates. These fundamental properties make it clear that gasoline is lighter than diesel and help ensure safe operations by understanding whether diesel or gas is heavier.
Is Diesel Thicker Than Gas?
- If you’ve ever wondered if diesel is thicker than gasoline, the answer is yes, with diesel’s viscosity at 104F typically ranging from 1.9- 4.1centistokes.
- Gasoline’s viscosity is considerably lower, generally less than one centistoke, which consistently makes diesel thicker than gas across all grades.
- This higher viscosity significantly impacts various engine functions, including injection timing, the atomization of the spray, and the lubrication requirements for the pump.
- Cold weather naturally increases viscosity, necessitating the use of winterized diesel and heaters to ensure proper fuel flow.
- For drivers curious about whether diesel is thicker than gasoline, this difference means expecting slower cold cranking and different filter strategies are needed.
- In contrast, the lower viscosity of gasoline is well-suited for high-RPM, spark-ignition engine designs.
- ASTM standards establish the viscosity boundaries for #2 diesel, which are crucial for protecting pumps and injectors throughout all seasons.
Is Diesel Denser Than Gasoline?
Yes, diesel is denser than gasoline, based on typical ranges at 59F. Diesel generally ranges from roughly 6.84-7.34lbs per U.S. gallon. In contrast, gasoline spans approximately 5.92- 6.43 lbs per U.S. gallon. This higher density means that diesel delivers more energy per liter, which is important for the torque generated in compression ignition engines. This also explains why diesel is heavier than gasoline when you consider it in terms of real-world fueling and logistics.
Is Diesel Heavier Than Gas?
Diesel typically weighs more per gallon and has higher density and viscosity than gasoline, which affects payload limits, engine design, and cold-weather handling. Learn how temperature-corrected values, density ranges, and seasonal blends impact real-world fueling and compliance.
Are Diesel Engines Heavier Than Gas?
If you’ve ever wondered whether diesel engines are heavier than gas engines, the answer is generally yes when comparing engines in similar vehicle classes. This is because diesel engines are built with reinforced blocks, stronger pistons, and higher compression ratios. They also often include turbochargers to handle the intense peak cylinder pressures. This added mass isn’t just for show; it contributes to their durability and ability to deliver powerful torque, especially useful for towing and demanding, long duty cycles.
In contrast, gasoline engines are lighter and designed to favor higher revolutions per minute (RPMs), relying on spark ignition for combustion. The heavier structure of a diesel engine gives it superior low-speed pulling power and a longer lifespan, though this can mean a higher initial cost. These engineering choices are a direct reflection of the properties of the fuel and how combustion occurs. So, when considering which is heavier, gasoline or diesel engines, diesel designs typically come out on top due to these specific components and the pressure demands they face. The trade-off for this added weight is often greater efficiency and longevity, especially when operating under a heavy load.
Does Gas Float On Diesel?
Gasoline is indeed lighter than diesel, a fact attributed to its lower density. When gasoline and diesel are mixed in a container, the gasoline will float on diesel, creating distinct layers. This separation in tanks can cause issues with fuel pickup, filtration, and proper combustion. Accidental mixing also carries the risk of poor ignition quality and potential pump damage. If you’re wondering whether diesel or gas is heavier, density tables consistently show diesel as the denser, heavier fuel, which explains this layering phenomenon. To prevent such problems, it’s crucial for storage managers to avoid mixing fuels, use proper labeling, and employ separate transfer equipment. If contamination does occur, the tank should be isolated, and a fuel service contacted for safe handling and corrective actions to prevent downtime and equipment damage.
Does Water Sink Or Float In Diesel?
Because water is denser than diesel, it naturally sinks to the bottom of fuel tanks. This settled water can cause significant problems, including the corrosion of tanks, providing a breeding ground for microbes, and ultimately leading to filter plugging. To prevent these issues, many fuel systems are equipped with water separators and drain points designed to remove accumulated water before it can reach critical components like injectors. Regularly checking for water and implementing fuel polishing techniques are crucial steps to reduce these risks. This is especially vital in situations where storage conditions frequently change or when fuel is stored for extended periods.
How Long Does It Take For Gas And Diesel To Separate?
Separation occurs quickly once flow stops because density differences drive stratification. Agitation temporarily disperses droplets, but layers reform over minutes to hours depending on temperature, mixing intensity, and additive chemistry. Additives may slow or modify separation, but they do not fix cross fuel contamination risks. The safest response is to isolate, pump out, and professionally dispose.
Can Diesel And Gasoline Be Mixed?
Do not mix. Even small volumes change ignition quality, lubricity, and detonation behavior. Gasoline in diesel reduces lubrication and harms pumps and injectors. Diesel in gas disrupts spark ignition and can foul plugs and catalysts. If mixing occurs, stop the engine, do not start, and arrange a tank drain and system flush immediately. Follow local disposal rules.
How To Tell If There Is Gas In Your Diesel?
Watch for hard starts, knocking, reduced power, and pump noise. Fuel may smell lighter and lose lubricity. Check with a simple jar test to observe layering and send a lab sample for confirmation. If positive, avoid running the engine. Drain the tank, replace filters, and refill with clean fuel. Consider fuel polishing where feasible.
Mixed Gasoline And Diesel?
Gasoline floats on diesel and even small cross-contamination can harm pumps, injectors, and ignition quality. If mixing occurs, stop the engine, isolate the tank, and arrange a drain and flush, then replace filters and refill with clean fuel.
Why Is Diesel Heavier Than Gasoline?
Diesel, comprised of larger and heavier hydrocarbon chains from later stages of refinery distillation, is inherently denser than gasoline, which comes from lighter fractions. This heavier composition is crucial for its function in compression ignition engines, as its slower vaporization and longer carbon chains release significant energy under high pressure. This fundamental chemistry explains why diesel is heavier than gasoline and why diesel is denser than gasoline across all markets. Even with seasonal blending adjustments for volatility, diesel’s weight per gallon consistently remains above gasoline. To understand what is heavier diesel or gasoline, it’s best to consider their density and the specific distillation windows from which they are derived, rather than superficial characteristics like color or smell. These consistent properties are essential for carriers to accurately calculate loads and correct volumes based on temperature, while refinery practices and fuel standards ensure predictable performance.
What Factors Influence Gasoline’s Weight?
The weight of gasoline isn’t a fixed number, it changes depending on its chemical makeup, how many aromatic compounds it contains, if it’s blended with ethanol, and even on its temperature. Generally, a good reference point for its density is about 6.3lbs per gallon at 59F, but this can really shift based on where you are and the time of year. For instance, gasoline with more aromatics will be denser and, therefore, weigh a bit more. When ethanol is mixed in, it affects both the energy content and the overall mass per gallon. To keep things consistent for transactions and when transferring custody, we use volume correction factors that adjust everything to a 59F basis.
For drivers who are curious about whether gas is heavier than diesel or if gasoline is lighter than diesel, the simple answer is that gasoline is indeed lighter. Even when comparing premium versus regular gasoline, there are slight differences in density, which are linked to their specific formulations. To ensure accuracy in planning, it’s always best to use volume data that’s been corrected for temperature and to check verified density information from your suppliers or reference tables.
Weight Of Gasoline Per Gallon
| Measure | Typical Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Weight per US gallon | Approximately 6-6.3lbs | Based on density 5.92-6.42lbs per gallon at 59F |
| Weight per liter | 1.56-1.7lbs | Composition and aromatics fraction influence density |
| Temperature correction | Use 59F reference | Apply volume correction factors for custody transfer |
| Comparison to diesel | Diesel 7-7.2lbs per gallon | This confirms that diesel is heavier than gasoline in practical terms. |
Why Is Diesel Better Than Gas?
- Diesel engines deliver strong low speed torque for towing and heavy loads.
- Compression ignition improves part load efficiency versus spark ignition gasoline.
- Diesel has higher volumetric energy, aiding range and fuel economy.
- Robust construction supports long life in commercial duty cycles.
- Modern aftertreatment reduces emissions while retaining durability.
- For fleets asking is diesel or gas heavier, heavier fuel and engines aligned with hauling tasks.
- Total cost depends on duty cycle, fuel prices, and maintenance planning.
Worried About Water In Your Diesel?
Water is denser than diesel and sinks to the bottom of tanks, leading to corrosion, microbes, and plugged filters. Use separators, routine draining, and fuel polishing to protect equipment and reduce downtime.
What Is The Fundamental Difference Between Diesel And Gasoline?
The diesel and gasoline are both derived from crude oil through refining processes, however, they have very fundamental differences. Which we explore in this table;
| Feature | Diesel | Gasoline |
|---|---|---|
| Ignition Type | Compression ignition | Spark ignition |
| Density | Higher | Lower |
| Cetane/Octane | High cetane (readiness to ignite) | High octane (resistance to knock) |
| Engine RPM | Favors low RPM (torque) | Suits high RPM (power) |
| Combustion | Lean burn conditions | Throttle control |
| Applications | Hauling, heavy-duty tasks | Lighter duty tasks, urban stop-and-go |
| Related Properties | “Is diesel fuel heavier than gas?” | “Is gasoline or diesel heavier?” |
| Key Design Influence | Injection strategies, compression ratios, turbocharging choices, lubrication demands | Injection strategies, compression ratios, turbocharging choices, lubrication demands |
Petrol Vs Diesel Refinery Processing
Refineries separate crude into fractions by boiling range. Petrol or gasoline originates from lighter fractions with lower boiling points, while diesel comes from heavier distillates. Additional processes like reforming, hydrotreating, and blending tune octane for petrol and cetane for diesel. Heavier molecules in diesel explain which is heavier petrol or diesel because molecular weight and structure raise density. Seasonal blending adjusts volatility and cold flow properties. These refinery pathways ensure consistent ignition behavior and emissions control compatibility in modern engines. Understanding the refining processes helps avoid confusion around which is heavier diesel or petrol by linking mass to distillation cuts.
Cetane Number In Diesel Combustion
Cetane number indicates how readily diesel ignites after injection. A higher cetane shortens the ignition delay, leading to smoother pressure increases, better cold starts, and reduced engine noise. Unlike gasoline’s octane, which resists knock, cetane promotes timely combustion under compression. Adequate cetane supports efficiency and minimizes white smoke during startup. This property is connected to whether diesel is denser than gasoline and its overall combustion. Fuel standards, like ASTM specifications, ensure engines run reliably across various temperatures. Maintaining proper cetane protects injectors and aftertreatment systems by stabilizing combustion.
Comparing The Energy Potential Of Diesel And Gasoline
Ever wonder why diesel cars often get better mileage than gasoline ones? It’s because, per liter, diesel carries more energy due to its higher density. This is why the perception that diesel is heavier than gas often correlates with better range. While energy per mass is similar, diesel retains an advantage on the road because of its volumetric energy. When considering gas or diesel for your vehicle, think about your driving habits, price, and aftertreatment requirements, as these factors, along with fuel blends, truly dictate performance and emissions.
How Diesel And Gasoline Impact Engine Design And Systems
The fundamental characteristics of fuels significantly influence the design of critical engine components, including fuel injectors, compression ratio, turbocharger sizing, and emissions control systems. Diesel engines, for instance, rely on high-pressure common rail injection systems and robust pumps that can handle the specific lubricity requirements of diesel fuel. They also often incorporate advanced aftertreatment systems like particulate filters and selective catalytic reduction to manage emissions.
On the other hand, gasoline engines prioritize precise spark timing, sophisticated knock control mechanisms, and the use of three-way catalysts. These distinctions in design and operation help explain why diesel engines are often heavier than gasoline engines. The inherent thickness of diesel, compared to gasoline, is also a crucial factor as it impacts pump wear and the fuel’s ability to flow efficiently in cold conditions. Regardless of the fuel type, proper storage and filtration are essential for maintaining optimal fuel performance and engine longevity.