Key Takeaways
- For trucks, cars and construction equipment, diesel #2 is the most common
- Diesel #1 is better for cold weather, diesel #2 has more energy.
- Round the year, diesel two offer more power, efficiency and low cost
- Diesel no 2 when designated for off-road use and exempt from tax is dyed red.
- In winter, it is common to mix diesel #1 and diesel #2 for better performance.
Table of Contents
What Is Diesel #2?
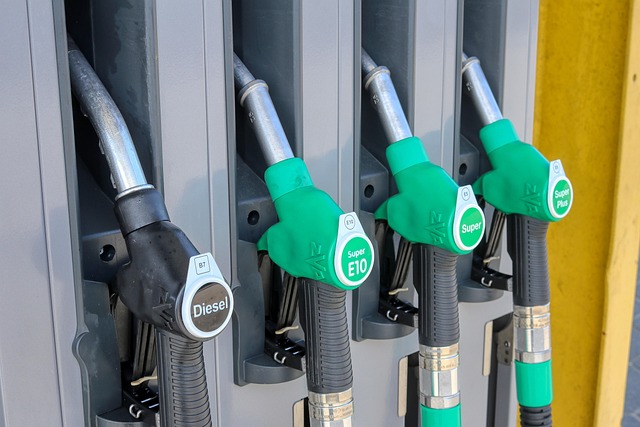
Diesel # 2 also known as diesel no 2 or number 2 diesel is a product of crude oil which is refined to be used in compression ignition engines. In comparison to diesel #1, diesel #2 has more energy per gallon, is more dense and more economical in heavy duty diesel engines. It has long hydrocarbon chains in its chemical structure, permitting higher deliveries of energy when burned but also makes it to easily gel in cold weather.
Given its versatile, diesel #2 is the preferred fuel for trucks, buses, farm and construction equipment. It is affordable, and very available, making it the most practical fuel for everyday use. To maximize cost efficiency if you have operations that consume large amounts of fuel, you should talk to several suppliers to secure the best deal on diesel #2.
What Does Diesel #2 Mean?
People have consistently wondered what diesel # 2 means in fuel teams. Well, the #2 designation refers to the grade in the diesel fuel number classification system. The designations are based on how the fuels perform in certain conditions. For example; number 1 diesel is lighter, more refined and is more resistant to gelling in cold temperatures, while number 2 diesel is thicker, delivers more energy but easily gels in cold weather. Number 2 diesel is best for standard operating conditions.
Diesel no 2 is more energy dense, therefore, it is more appropriate for heavy duty applications that involve hauling heavy loads over long distances. It is also widely available, so its prices are usually lower. However, diesel # 1 is mostly used in the winter seasons or they mixed with diesel #2 to prevent it from gelling. So, the diesel number denotes how the fuel performance is under specific weather and usage conditions.
Wondering If Diesel #2 Is Right for Your Truck?
Diesel #2 is the standard fuel for most trucks, SUVs, and heavy-duty equipment. Learn when to stick with #2, when to switch to #1 in cold weather, and how winter blends protect your engine.
What Color Is Number 2 Diesel?
Number 2 diesel is typically clear or of slightly amber coloration. As earlier mentioned, number 2 diesel is the most available fryer of diesel and it’s usually sold at fuel stations. When sold at fur stations it appears in its natural color (not dyed) because it is for on-road use and is subject to taxes for highway use. However, when used in off-road applications, diesel #2 is dyed red. This coloration has nothing to do with performance or chemical properties and everything to do with regulation. Diesel no 2 dyed red is not taxed and is specifically used for off-road applications such as in agriculture, mining or construction.
The difference in color between clear #2 diesel and red dyed #2 diesel is mainly a matter of tax regulation which permits vehicles and equipment in off-road applications to function at lower costs than on-road vehicles.
What Is The Diesel Number?
When you hear “diesel number”, it could leave you confused because it could either be referring to the cetane number or the fuel grading number. In this article, we use the diesel number for the purpose of fuel grading based on fuel performance in different conditions. The cetane number is used to measure how easily diesel burns under compression (ignition quality).
So if you ever hear about the diesel number, make sure to clarify if it refers to number 1 diesel and number 2 diesel or the cetane rating.
What Is #1 Diesel?
The characteristics of diesel no 1, also known as diesel #1 or number 1 diesel are;
- It is lighter
- It is more refined
- It has a very low gelling point so it flows well in cold temperatures.
- Less energy density
- Cost more per gallon
Diesel # 1 due to its extremely low gelling point is very ideal for cold temperatures and is sometimes mixed with #2 diesel in winter to make it last longer. However, throughout the other seasons of the year, diesel #2 is the preferred fuel used.
Paying Too Much for Diesel #2?
Prices for diesel #2 can shift with crude oil, taxes, and seasonal blends. Fleet operators and farmers can save thousands by comparing suppliers and exploring red diesel for off-road use.
Are Kerosene And #1 Diesel Actually The Same?
Kerosene and diesel #1 are have a lot of chemical similarities as higher are light distillates with low gelling point making them suitable for winter. But kerosene is very light, lighter than diesel #1 and has very little lubrication. Even though kerosene can be used in some emergency situations in some engines, it is no substitute for diesel #1 as it lacks lubrication properties that are crucial for engines.
So while born have very similar chemical properties, they cannot be used interchangeably. Where diesel # 1 is needed, don’t use kerosene.
Diesel #1 Vs. Diesel #2
| Feature | Diesel # 1 | Diesel # 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Content | Lower BTUs per gallon | Higher BTUs per gallon |
| Cold Weather Performance | Fluid at low temperatures | Gels at low temperatures |
| Viscosity | Thinner and lighter | Thicker and denser |
| Cost | Usually more expensive | More affordable |
| Typical use |
|
|

Can You Mix #1 Diesel And #2 Diesel?
Yes! Mixing diesel #1 and diesel #2 is actually a very common and approved practice. In winter, when suppliers sell what is called “winter diesel”, it is essentially a blend of number 1 and number 2 diesel. This is done to maintain the higher energy density of diesel # 2 while maintaining the fluidity of diesel #1.
Winter blends are just the mixture of the two numbered diesels. However, this is mostly only done in winter because during the rest of the year, most drivers and fleet operators prefer using diesel #2.
Can I Safely Use Diesel #2 In My Truck?
The short answer to the question of whether you can use diesel #2 in your truck is yes! Not only will diesel #2 be compatible with your pickup, SUV or heavy-duty truck, it is the recommended fuel type for you because it is high in energy density and due to its availability, is considerably cheap.
Sometimes, manufacturers will recommend you switch to diesel #1 during winter due to its low gelling point.
For semis, sprinter vans and agricultural equipment, diesel # 2 is the preferred option. Not only is it more energy efficient but it also helps you maintain warranty conditions, ensuring long term engine health. It is advisable to always check the recommendations of the manufacturer in the user’s manual.
What Is The Difference Between Premium Diesel And #2 Diesel?
Premium diesel is diesel #2 with additives slaughtered as detergents, lubricant and a higher cetane ratings. The roles of these additives are to clean injectors, improve ignition and reduce emissions. Premium diesel is usually more performant and economical than diesel #2 and also helps extend engine life.
If you burn high performance vehicles, it may be beneficial to use premium diesel. Nonetheless, diesel #2 is the most commonly used fuel as it balances cost and performance well.
To know which one to use, test premium diesel and compare to diesel #2.
Confused About Red Diesel vs Clear Diesel?
Clear diesel fuels your road vehicles, while red diesel powers off-road equipment tax-free. Using the wrong type could mean fines. Get clear guidance on which fuel to use where.
Which Type Of Diesel Is More Environmentally Friendly?
- The cleanest fuel types are renewable diesel or the biodiesel mixes.
- Diesel # 1 and Diesel # 2 have very little differences when it comes to reduced emissions and eco-friendliness
- Premium diesel has less emissions due to the additives it contains.
To reduce carbon emissions in number 2 diesel, it can be mixed with biodiesel and renewable diesel. The B20 blends which comprise 20% biodiesel, 80% diesel # 2 are increasingly being used at the greener alternatives to diesel #2.
But for reasons of availability and cost effectiveness, diesel #2 is still the most widely used fuel type.
What Is The Cloud Point Of #2 Diesel?
In cold weather, the paraffin wax in diesel #2 can start to crystallize, when these crystals are many, they make the fuel look cloudy. The temperature at which this happens is called the cloud point of diesel #2. This typically happens at approximately 14F, and diesel #2 thicken, can clog fuel filters leading to the engine stalling.
This is why some drivers switch to diesel #1 in winter or blend it with diesel 2. Knowing this can save your vehicle during winter, permitting it to operate normally and avoiding the engine from knocking.
Is Diesel #2 Only For Summer?
Due to the cloud point of diesel #2, it is mostly used during warmer seasons when it doesn’t run the risk of gelling.
During the colder months, diesel #2 is usually blended with diesel #2 to keep the high energy density of number 2 diesel and to lower its cloud point and ensure smooth engine performance.
Is #1 Or #2 Diesel Considered Red Diesel Fuel?
Number 1 diesel and number 2 diesel are only dyed red if they are destined for off-road use.
Diesel is dyed for off-road use because when used off-road for farming, construction or mining activities, it benefits from some tax exemptions that permit those industries to enjoy lower fuel costs.
Diesel #2 is usually the one that is dyed. So yes, #2 diesel is red diesel but only when dyed. And when it is dyed, it is reserved only for off-road use.
Using dyed diesel on public roads will lead to fines and even criminal charges.
Is Number 2 Diesel Used For Off-Road?
Yes, #2 diesel is used off-road. Mainly industries such as agriculture, mining and construction. When this happens, the diesel #2 is dyed red to make it easily recognizable and to qualify it for the defined tax exemptions on off-road diesel.
What Is Diesel #2 Used For?
Due to its high energy density, low cost and ready availability, diesel #2 is used in the following machines and industries;
- Tractors for agriculture
- Long haul freights
- Buses and locomotives for transportation
- Generators for backup power in construction, mining and agriculture
- Industrial machinery in factories.
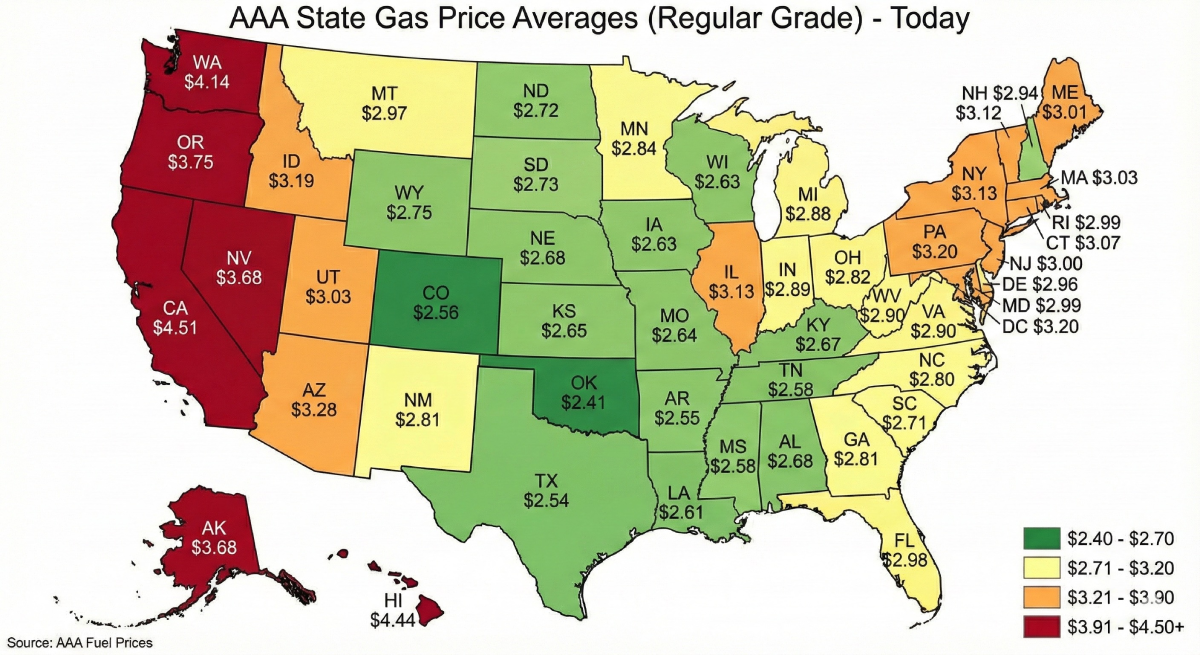
What Are The Costs Of Diesel #2?
As every fuel type that is gotten from crude oil, the price of diesel #2 fluctuates depending on the cost of crude oil, refining capacity and the amount of supply in relation to demand at any season.
In winter, prices usually go up as refineries adjust blends, regional taxes also affect the prices of fuel and so does distribution cost.
Diesel #2 Vs. Gasoline
- Diese #2 and gasoline differ firstly in the types of engines they serve. And also differ in performance and usage.
- Gasoline engines are designed to rely on spark plugs to ignite
- Diesel engines compress air to ignite
- Diesel number 2 engines provide more torque and are more economical
- Gasoline engines accelerate faster
Gasoline and diesel #2 are absolutely not interchangeable. Using one in the engine of the other will destroy the engine.