Key Takeaways
- Fuel use scales with watts and load, not just tank size.
- Light load saves fuel, but very light loads can waste fuel on big units.
- A typical 2,000 W inverter uses about 0.1-0.2 gal/hr at 25-50% load.
- Whole-home standby on gasoline is rare; most use natural gas or propane.
- Store fuel safely, rotate stock, and plan for refueling during long outages.
Table of Contents
How Much Gas Does A Generator Use
Fuel use depends on generator type, displacement, and the percentage of rated load. Fuel use varies with altitude, temperature, ethanol blend, maintenance, and specific engine efficiency.
Typical gasoline usage by category (estimates at sea level):
- 1,000-2,200 W inverter portables: ~0.08-0.25 gal/hr at 25-50% load.
- 3,000-4,500 W mid-size portables: ~0.2-0.45 gal/hr at 25-50% load.
- 5,000-7,500 W open-frame portables: ~0.4-0.9 gal/hr at 25-75% load.
- 8,000-12,000 W large portables: ~0.6-1.2 gal/hr at 25-75% load.
- Gasoline standby (less common): varies, but expect 0.8-1.6+ gal/hr near 50-100% load.
How Much Gas Does A Generator Need?
Calculate what to keep on hand using your typical daily hours and load.
Manual method:
- Estimate average load (W). Add the watts of devices that run most of the time.
- Pick a generator size. Target 50-70% of rated output under steady use.
- Find a burn rate for that load from the tables in this article.
- Multiply by hours: Gallons/day = burn rate (gal/hr) × hours/day.
Key factors:
- Load size: Higher load increases fuel use nonlinearly.
- Engine efficiency: Inverter models often beat open-frame units at light loads.
- Run hours: Overnight runs consume more than you expect. Use thermostats and timers.
How Many Gallons Do You Need for 24 Hours?
Use the fuel burn ranges in this guide to plan storage. Pick your load, find the gal/hour estimate, then multiply by run hours. Example: a 2,000 W inverter at 25% load uses about 0.1 gal/hour, while a 7,500 W open frame at 50% uses about 0.6 gal/hour.
Portable Generator Fuel Consumption
Portable units span small inverters to open-frame worksite models.
Typical usage:
- 2,000 W inverter:
- 25% load: ~0.1 gal/hr.
- 50% load: ~0.18 gal/hr.
- 3,500-4,000 W mid-size:
- 25% load: ~0.2 gal/hr.
- 50% load: ~0.35-0.4 gal/hr.
- 6,500-7,500 W worksite:
- 25% load: ~0.35-0.45 gal/hr.
- 50% load: ~0.55-0.7 gal/hr.
- 75% load: ~0.8-0.9 gal/hr.
Common emergency loads and examples:
- Fridge + lights + Wi-Fi: A 2,000 W inverter in eco mode may run 8-14 hours per gallon, depending on weather and cycling.
- Sump pump + fridge + TV: A 3,500 W unit may run 3-5 hours per gallon at ~30-40% load.
- A portable heater is risky indoors. Prefer electric blankets or oil-filled radiators with proper ventilation and safe circuits.
Gasoline Generator Fuel Consumption
Gasoline models vary widely. Quality, tuning, altitude, and fuel grade matter.
Consumption ranges:
- Small inverter (1-2.2 kW): 0.08-0.25 gal/hr at 25-50%
- Mid portable (3-4.5 kW): 0.2-0.45 gal/hr at 25-50%
- Large portable (5-7.5 kW): 0.4-0.9 gal/hr at 25-75%
Fuel grade and quality impact:
- Use fresh gasoline and stabilize for storage beyond 30 days.
- E10 is common; keep water out and store in sealed containers.
- Stale fuel causes hard starts and higher consumption.
- Altitude and temperature shift mixture needs. Check carb jets or EFI settings per the manual.

How Much Fuel Does A Generator Use In 24 Hours?
Multiply your hourly rate by 24, then add refueling downtime if the tank is small.
Full-day estimates, continuous operation:
- 2,000 W inverter at 25% load (0.1 gal/hr): ~2.4 gallons/day.
- 3,500 W portable at 40% load (0.3 gal/hr): ~7.2 gallons/day.
- 7,500 W open-frame at 50% load (0.6 gal/hr): ~14.4 gallons/day.
- 10,000 W portable at 50% load (0.8 gal/hr): ~19.2 gallons/day.
For multi-day outages, split storage into multiple 5-gal containers. Label and rotate stock every 3-6 months with stabilizer.
How Much Fuel Does A Small Generator Use?
Small inverters are efficient at light loads.
Under light to moderate load:
- 1,000-1,600 W inverters can use 0.06-0.15 gal/hr at 20-40% load.
- Expect 8-16 hours on a gallon when powering only essentials like a fridge, lights, router, and phone charging.
Advantages:
- Quiet operation.
- Safe for electronics.
- Excellent fuel economy in eco mode.
Inverter vs Open Frame for Fuel Savings
At light to medium loads, inverters often use less gas than open frame units. Compare your typical watts to the tables, target 50 to 70 percent of rated output, and see where eco mode and right sizing cut consumption.
How Much Fuel Does A Generator Hold?
Tank size controls run time between refills.
Typical gasoline tank sizes:
- Small inverter (1-2.2 kW): 0.6-1.2 gallons.
- Mid portable (3-4.5 kW): 2.0-4.0 gallons.
- Large open-frame (5-7.5 kW): 5.0-8.0 gallons.
- Very large portable (8-12 kW): 7-10+ gallons.
Run time (hours) ≈ Tank size ÷ burn rate. Always keep a safety margin and avoid running dry, which can damage appliances during a sudden stop.
How Long Will 1 Gallon Of Gas Run A Generator?
It depends on engine size and load.
Rule-of-thumb run times on 1 gallon:
- 2,000 W inverter at 25% load: 8-12 hours.
- 3,500 W portable at 30-40% load: 2.5-4 hours.
- 7,500 W open-frame at 50% load: 1-2 hours.
Use cases for small quantities:
- Short evening runs to chill a refrigerator and recharge devices.
- Test runs for maintenance without wasting fuel.
- Light overnight loads with a quiet inverter in eco mode.

How Long Do 5 Gallons Of Fuel Last In A Generator?
Depending on the load, 5 gallons can last for varied hours in a generator
Typical results:
- 2,000 W inverter at 25% load (0.1 gal/hr): ~50 hours.
- 3,500 W portable at 40% load (0.3 gal/hr): ~16-17 hours.
- 7,500 W open-frame at 50% load (0.6 gal/hr): ~8-9 hours.
Partial vs full load:
- At 25-40% load, inverters stretch fuel significantly.
- Full load on big portables burns fuel quickly and is noisy. Balance loads or cycle appliances.
How Much Does It Cost To Run A Generac Generator For 24 Hours?
To calculate use the formula, cost = price per gallon × gallons per hour × 24 for gasoline. For natural gas, convert cubic feet to cost using your utility rate.
Example, Generac-type home standby on natural gas (illustrative):
- 14 kW unit at 50% load may use ~195 ft³/hr at 50% and ~256 ft³/hr at 100% on natural gas
- Gas price $1.20/therm (100 cu ft ≈ 1 therm for planning).
- Daily cost ≈ 1.2 × 24 × 1.25 ≈ $36.
Actual specs vary by model, altitude, and temperature. Use the formula with your utility price.
What Will It Cost to Run All Day
Turn gallons per hour into dollars with a simple formula. Cost equals fuel price times burn rate times hours. Get best and worst case estimates and plan refueling with safe storage and stabilizer.
How Long Will A Honda EU2200i Run On A Tank Of Gas?
The EU2200i is known for its excellent economy. With a tank around 0.95 gallon, real-world run time varies by load and eco mode.
Typical ranges:
- 25% load, eco on: ~8-10 hours per tank.
- 50% load, eco on: ~4-6 hours per tank.
- Higher loads: ~3-4 hours per tank.
Keep air filters clean, use fresh fuel with stabilizer, and enable eco mode to extend run time.
How Much Gas Does A Generator Use To Power Your House?
Whole-home use depends on what “whole home” means. Central AC, electric ranges, and well pumps raise load sharply.
Estimates:
- Essentials only (1-2 kW avg): Small inverter may use 2-4 gallons/day.
- Partial home (3-5 kW avg): Mid portable may use 6-12 gallons/day.
- Near full home (6-10 kW avg): Large portable may use 12-24+ gallons/day.
Partial backup runs refrigerators, lights, electronics, and a small AC or space cooling while full backup adds HVAC and cooking, which can triple fuel needs.
For safe transfer switches, sizing, and reliable refueling during extended outages, consider professional installation and a scheduled fuel plan through a trusted provider such as Elan Fuels.
How Much Natural Gas Does A Generator Use?
Natural gas is measured in cubic feet per hour (cfh) or therms.
Planning conversions:
- 1 therm ≈ 100,000 BTU ≈ ~100 cubic feet (utility billing varies).
- Small standby (7-10 kW): ~90-140 cfh at 50-100% load.
- Medium standby (11-16 kW): ~120-200 cfh.
- Large standby (18-24 kW): ~180-300 cfh.
Advantages for long-term use:
- No on-site refueling.
- Stable supply, cleaner burn, and quieter operation.
- Lower cost per kWh in many regions.
Factors Affecting How Much Gas Your Generator Uses
A couple of factors can affect how much gas your generator uses:
- Load size and variability.
- Engine type and efficiency (inverter vs open-frame).
- Altitude and temperature (air density).
- Maintenance (air filter, spark plug, oil).
- Fuel quality and freshness.
- Eco mode and automatic idle control.
- Power factor for motor loads and tools.
Small changes here can shift fuel needs by 20-40%
How Much Does It Cost To Run A Generator?
Generator operating costs vary: Daily cost = burn rate (gal/hr) × hours × fuel price.
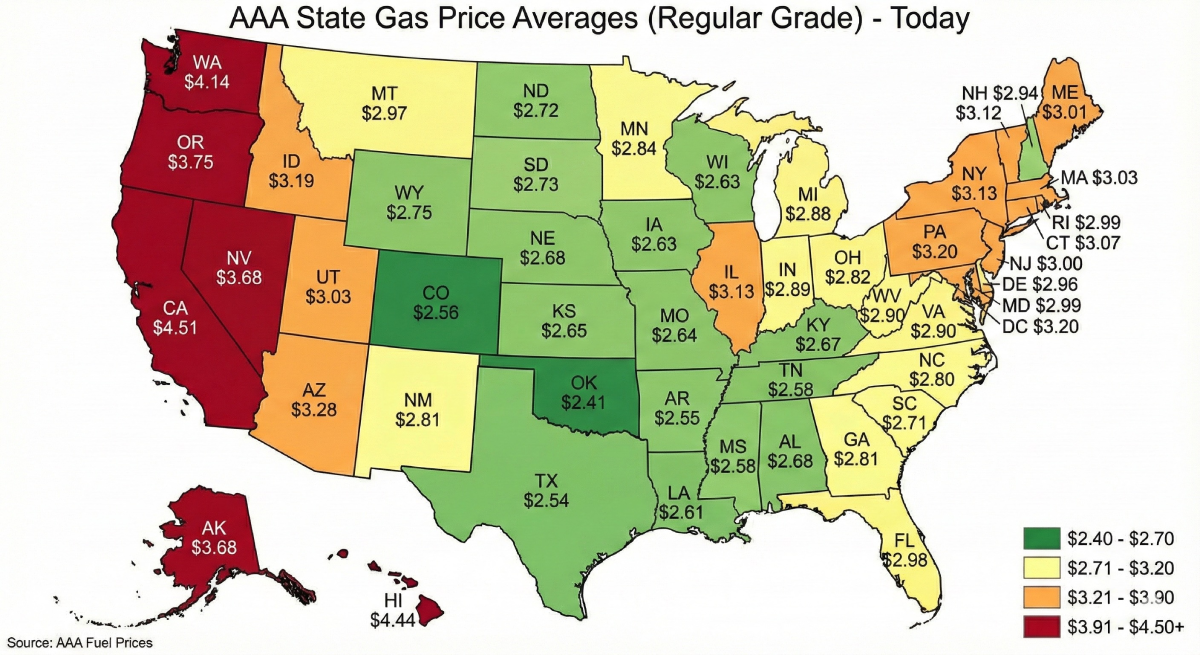
Examples (gasoline at $3.75/gal):
- 2,000 W inverter at 25% load (0.1 gal/hr), 12 hours: 0.1 × 12 × 3.75 = $4.50/day.
- 3,500 W portable at 40% load (0.3 gal/hr), 16 hours: 0.3 × 16 × 3.75 = $18.00/day.
- 7,500 W at 50% load (0.6 gal/hr), 24 hours: $54.00/day.
For natural gas, multiply cfh by your per-cf rate. For propane, use gallons per hour times $/gal.
Estimate best and worst cases. Store at least 2-3 days of fuel for portables, or verify gas line capacity for standby systems.
Generator Size And Output
Bigger generators burn more fuel, especially at higher loads. But oversizing too much can also waste fuel at idle.
Examples:
- 2 kW inverter: Best at 200-1,000 W continuous.
- 3.5-4.5 kW portable: Best at 800-2,500 W continuous.
- 7.5-10 kW portable: Best at 2,000-6,000 W continuous.
- 18-24 kW standby: Best at 5,000-15,000 W continuous.
Actionable ways to lower fuel use:
- Shift heavy loads so they do not overlap.
- Use eco mode for inverters.
- Add LED lighting and efficient appliances.
- Insulate refrigerators and minimize door openings.
- Use a transfer switch to safely prioritize circuits.
Gas Generator Fuel Consumption Calculator
You can calculate by hand or use online tools. Here is a simple method.
Manual calculator steps:
- List devices and their watts.
- Estimate average running watts, not just starting watts.
- Choose generator size and target 50-70% load.
- Select a burn rate from tables or your manual.
- Compute fuel: Gallons = burn rate × hours.
Keep a small log of hours, loads, and refills to refine your own rate.
Light Vs. Full Load
Fuel use rises as load rises, but efficiency can improve slightly up to a midrange point.
Comparison, 7,500 W portable (illustrative):
- 25% load (~1,875 W): ~0.35-0.45 gal/hr.
- 50% load (~3,750 W): ~0.55-0.7 gal/hr.
- 75% load (~5,625 W): ~0.8-0.9 gal/hr.
- 100% load: Often near 1.0-1.2 gal/hr, louder and hotter.
Load management tips:
- Cycle big appliances, avoid peak overlap.
- Use smart strips and timers.
- Favor inverter tools and ENERGY STAR appliances.
Diesel And Natural Gas Generator Fuel Consumption Charts
Use these sample tables for planning. Values are generalized.
Table 1: Diesel generator consumption (approximate)
| Output (kW) | 25% Load (gal/hr) | 50% Load (gal/hr) | 75% Load (gal/hr) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 0.25 | 0.35 | 0.5 |
| 10 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 1.1 |
| 20 | 0.9 | 1.5 | 2.2 |
| 50 | 2.1 | 3.5 | 5.0 |
Table 2: Natural gas generator consumption (approximate)
| Output (kW) | 50% Load (cfh) | 100% Load (cfh) |
|---|---|---|
| 7-10 | 90-140 | 120-200 |
| 14-16 | 120-180 | 180-260 |
| 20-24 | 160-230 | 220-320 |
How to read and apply:
- Pick your expected average load, not the nameplate.
- Interpolate between rows.
- Multiply by hours to get daily fuel.
- Convert cfh to therms if needed for billing.
Pros and cons by fuel:
- Gasoline: Easy to find, higher cost per kWh, storage limits.
- Diesel: Efficient, great at heavy load, longer storage life with proper treatment.
- Natural gas: Continuous supply, lower operating cost, professional install required.
Diesel Vs Gasoline Vs Natural Gas In Commercial Generators
Efficiency and cost:
- Diesel offers the best fuel-to-kWh conversion at heavy loads and long runtimes.
- Natural gas often wins on operating cost and logistics for fixed sites.
- Gasoline suits short, mobile tasks but is not the best for 24/7 duty.
Applications where each excels:
- Diesel: Construction sites, remote operations, prime power.
- Natural gas: Hospitals, telecom, data centers with long run requirements.
- Gasoline: Home emergencies, mobile crews, small events.
Emissions rules, noise limits, maintenance skills, and on-site safety practices.