Key Takeaways
- Heavier construction and lower revs explain why diesels run longer than gas engines in sustained work.
- Usage pattern decides which lasts longer diesel or gas, especially towing and highway miles.
- Clean fluids and intervals drive diesel vs gas engine life, preventing costly failures.
- Fuel traits support components, but build quality still leads diesel engine vs gas engine longevity.
- Maintenance discipline turns potential into real diesel engines that last longer than gas outcomes.
Table of Contents
Why Do Diesels Last Longer?
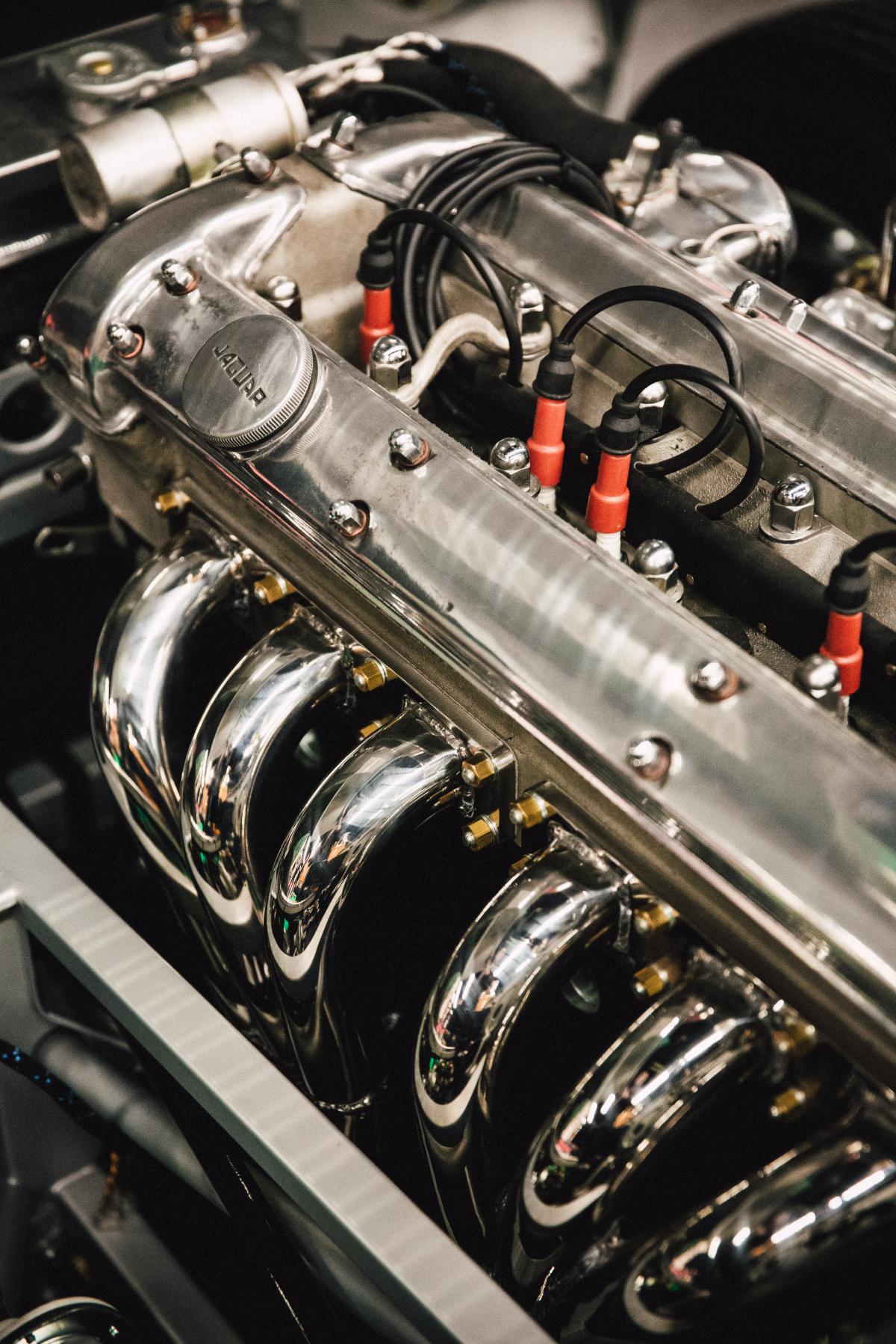
So, why do diesels last longer? It really comes down to a few key factors: their unique compression ignition system, incredibly strong build, and their tendency to operate at lower RPMs. That high compression ratio demands thick engine blocks and robust internal components, which inherently makes them more durable under heavy loads. The fact that they complete fewer revolutions per mile also significantly reduces the wear and tear on the engine, especially during highway driving and in commercial fleets. On top of that, efficient combustion and excellent lubrication systems work together to protect critical parts like bearings and rings.
However, it’s worth noting that the longevity of a diesel engine versus a gas engine isn’t absolute. It heavily depends on how the engine is used and maintained. When properly serviced, diesel engines definitely have a longer life, particularly in applications like towing and hauling. But if they’re misused, the differences in engine life between diesel and gas engines can narrow considerably. Ultimately, your choice should be based on the specific workload you anticipate.
Do Diesel Trucks Last Longer?
- Towing at low revs shows why diesels run longer than gas engines, since torque reduces downshifts and stress.
- Fleets report strong diesel engine vs gas engine longevity when trucks live on highways with steady loads.
- Light duty pickups may blur which lasts longer diesel or gas if used for short trips.
- Heavy duty platforms highlight diesel engines that last longer than gas with cooling and oil capacity.
- Proper service preserves diesel vs gas engine life under commercial cycles.
Build a Diesel Longevity Maintenance Plan
Turn potential into real life. Use miles and hours to set intervals, change filters proactively, and track trends with oil analysis to prevent wear before it starts.
Diesel Fuel Vs Gasoline?
This section covers fuel properties and storage life rather than engine construction. Diesel has higher energy density than gasoline, which supports steady work at lower revs and fewer refueling stops. These traits touch diesel engine vs gas engine longevity only indirectly by promoting duty cycles and temperatures.
Diesel lubricity can help pumps and injectors maintain films, reducing scuffing that undermines diesel vs gas engine life. Yet cleanliness rules lifespan. Water, oxidation, and microbes threaten filters and clearances during storage. Use tight filtration, water separation, and treated fuel. Match seasonal grades and rotate stocks.
How Do Diesel Design Features Help Engines Last Longer?
Ever wonder why diesels last longer in demanding roles? It all comes down to their robust design. Think about it: thick cylinder walls and rigid main webs are specifically engineered to stabilize the engine’s geometry even under immense pressure. This improved stability helps with better sealing and contributes to why diesel engines last longer than gas engines.
Another key factor in diesel versus gas engine life is the generous bearing areas and ample oil galleries. These features ensure that lubricating films are maintained even under heavy loads, which is crucial for longevity. Plus, conservative redlines keep the mean piston speed low, explaining why diesels run longer than gas engines, especially on long journeys.
Furthermore, the high-compression parts are built to resist fatigue, and targeted cooling systems work to limit thermal cycling. All these design choices collectively elevate diesel engine versus gas engine longevity, assuming proper maintenance. It’s worth noting, though, that this benefit can diminish with poor service or short bursts of heavy, idle use.
Towing Often?
Protect Your Engine While You Pull
High torque at low RPM reduces heat and stress. Keep radiators and charge-air paths clean and monitor coolant, oil, intake, and exhaust temps on every haul.
How Robust Construction Supports Diesel Longevity
Modern diesel engines are engineered with a focus on durability, a primary factor in explaining why diesels last longer than their gasoline counterparts. This longevity stems from a combination of robust materials, precise manufacturing, and design choices that prioritize endurance under demanding conditions. The table below outlines key structural features and their direct impact on diesel engine vs gas engine longevity, illustrating how these elements contribute to the extended operational life often observed in diesel vehicles.
| Feature | Description | Mitigation Point | Longevity Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thick decks and walls | Robust block architecture | Distortion and blow-by | Contributes to diesel engines outlasting gas |
| Reinforced mains | Rigid crankshaft support | Bearing overloading | Enhances diesel engine life over gas |
| Large bearings | Expanded film area | Metal-to-metal contact | Improves diesel engine longevity |
| Forged rods and pistons | High-strength components | Fatigue cracking | Explains why diesel engines last longer |
Diesel Engines And Higher Compression
One of the main reasons diesel engines last longer than gasoline engines in tough service is their higher compression. This fundamental design requirement for extreme pressures compels engineers to use stronger materials and build in generous safety margins, which significantly contributes to diesel engine vs gas engine longevity under heavy loads.
Additionally, the inherent thermal efficiency of diesel engines reduces waste heat and throttling losses. This, in turn, eases the stress on the oil and coolant systems over time. When you consider lower engine revolutions per minute (RPMs) at cruising speeds, it becomes clear why diesels run longer than gas engines, especially on intercity routes. All these factors combined explain why diesel engines last longer than gas, provided that regular maintenance aligns with both hours of operation and mileage. This balance ultimately explains which lasts longer, diesel or gas, when observed across real-world fleets.

Role Of Heavy-Duty Components In Diesel Longevity
Diesel engines are designed for longevity in daily use, featuring oversized bearings, stout rods, and robust pistons that maintain conservative loads. Their large journals help preserve oil film even at low revolutions per minute and high torque. The use of forged parts enhances their resistance to fatigue, a common challenge for gasoline engine designs. These combined design choices contribute to diesel engines lasting longer than gas engines when regularly serviced.
Diesel Engine Lubrication Features
High-capacity sumps, full-flow filtration, and piston cooling jets work together to maintain stable temperatures and film thickness under load. Essential bearings are supplied through targeted galleries, which helps preserve the longevity of both diesel and gas engines on extended journeys. Regular oil changes and consistent oil quality are crucial for preventing abrasive wear and varnish, thereby sustaining the well-known durability advantages of diesel engines.
Materials And Techniques That Reduce Corrosion
When we consider how long diesel engines and gas engines last, it’s clear that several factors play a role in their overall lifespan. For instance, choosing the right alloys, applying selective coatings, and carefully controlling the chemistry of the coolant are crucial for preventing corrosion, which can weaken seals and reduce the engine’s strength.
Beyond that, keeping fluids clean is essential for protecting the delicate tolerances of fuel injectors. This directly contributes to the longevity of both diesel engine and gas engine in modern vehicle platforms. Maintaining a balanced coolant system also safeguards cylinder liners and oil coolers, leading to real gains in a diesel versus gas engine life over many years of service.
Lower RPM And Its Impact On Engine Longevity
Diesel engines generally outlast gasoline engines, particularly in sustained operations.
- Reduced Wear: Diesel engines operate at lower average rotations per minute. This means fewer cycles per mile, which translates to less cumulative wear on critical components like rings, bearings, and valve trains, especially during highway driving.
- Lower Friction and Heat: At cruising speeds, diesel engines exhibit lower mean piston speeds. This reduces friction and heat generation, which is a significant advantage during demanding tasks like towing.
- Optimized Conditions: When combined with proper maintenance, such as clean fluids and effective temperature control, these inherent design characteristics further enhance the longevity of diesel engines.
enhance the longevity of diesel engines.
However, in stop-and-go urban driving, the longevity advantage of diesel engines diminishes
Diesel Engine Performance Through Higher Torque
You might wonder why diesels run longer than gas engines, especially when it comes to towing. It boils down to the high torque at low RPMs that allows diesel engines to perform the same amount of work with fewer revolutions. This not only reduces friction and lowers heat, but it also lessens the stress on engine films and hardware, significantly improving diesel vs gas engine life under heavy loads. Furthermore, their smooth drivability helps avoid frequent downshifts and high RPM spikes, reinforcing diesel engine vs gas engine longevity, particularly in hilly terrain. These inherent traits are why diesel engines last longer than gas engines in scenarios where trailers and payloads are a routine part of the job. However, for light commuter use, the benefit regarding which lasts longer, diesel or gas, is less pronounced.
Keep Heat in Range to Extend Engine Life
Stable temperatures preserve oil film and materials. Use OBD or gauges to watch coolant, oil, intake, and EGT, then act before heat damages bearings and rings.
Key Self-Cooling Features In Diesel Engines
Thanks to features like piston oil squirters and dense coolant passages, heat is efficiently removed right where it’s generated. This not only stabilizes components but also helps maintain critical lubricant films. Operating at cooler temperatures significantly slows down both lubricant oxidation and material fatigue. This is a key factor in diesel engine vs gas engine longevity, especially during demanding, long-haul cycles. Effective heat management truly underpins why diesels last longer when they’re consistently subjected to heavy loads and steep grades.
Why Is Diesel Engine Maintenance Crucial To Longevity?
Understanding why some engines outperform others can save you time and money.
Here’s a closer look at what gives diesel engines an edge:
- Maintenance transforms potential into real results, meaning diesel engines last longer than gas engines when properly cared for.
- Fluids and filters are crucial protectors in modern systems, directly impacting diesel vs gas engine life.
- Following recommended intervals by miles and hours clearly explains which lasts longer: diesel or gas engines in fleets.
- Early diagnosis after repairs reveals why diesels run longer than gas engines.
- Book an inspection to extend your diesel engine vs gas engine longevity today.
How Routine Maintenance Extends Diesel Engine Life
If you’ve ever wondered why diesels last longer than gas engines, it really comes down to meticulous maintenance. By carefully planning service intervals based on miles, hours, and even fuel consumed, you can mitigate risks and ensure longevity across all your routes. Regularly tracking services like oil, fuel, air, and coolant changes, and then cross-referencing those trends with used oil analysis, provides critical insights into protecting your diesel engine vs. gas engine longevity. Don’t wait for a restriction to trigger starvation; replace filters proactively to prevent shortening diesel vs. gas engine life. Also, remember to inspect belts, hoses, and charge air paths, as stable temperatures are crucial. Finally, maintaining comprehensive records isn’t just good practice; it also provides proof of care, which can be a significant asset when it’s time to sell. These diligent steps are key to making diesel engines last longer than gas, whether you’re operating light-duty or heavy-duty vehicles.
How To Manage Diesel Coolant, Oil, Air, And Exhaust Temperatures
Use gauges or on-board diagnostics to watch coolant, oil, intake, and exhaust temperatures. Keeping heat in range preserves film strength and materials, supporting diesel engine longevity over gas engine longevity. To prolong the life of both diesel and gas engines, regularly clean radiators and charge air coolers.
What To Expect From Diesel Engine Lifespan?
Have you ever wondered why diesels last longer than their gasoline counterparts? It’s a common observation, especially when you consider light-duty diesels that can achieve impressive mileages with proper care. This really highlights why diesels last longer in the right applications. When we look at medium and heavy-duty platforms, the evidence for diesel engine vs gas engine longevity in commercial use is even stronger, as these vehicles often rack up enormous hour counts. So, how do we fairly judge which lasts longer, diesel or gas? It’s not just about the odometer reading; defining high mileage should really be about the vehicle’s condition.
To truly assess diesel vs gas engine life in used trucks, you need to evaluate factors like compression, oil pressure, and the presence of smoke, along with a thorough review of service records. Many fleets can attest that with diligent fluid changes and consistent loads, diesel engines last longer than gas engines.
Which Diesel Engine Types Last The Longest And Why?
Diesel engines often exhibit greater longevity in real-world applications, particularly those with conservative specific output and ample cooling. Their simpler fuel systems are less susceptible to contamination, contributing to their extended lifespan compared to gas engines. The differences in engine life between diesel and gas engines are particularly pronounced in applications involving steady loads and low revolutions per minute. To determine which type of engine will last longer in a given scenario, it’s crucial to match the engine family to its intended duty cycle. When paired with consistent maintenance based on hours of operation and seasonal changes, achieving a longer lifespan with diesel engines than with gas engines is a realistic outcome.
What Makes TDI Diesel Engines Last Longer?
Small displacement turbodiesel engines are known for their efficient torque delivery at low revolutions per minute, which contributes to their extended lifespan compared to gasoline engines in both commuter and highway driving scenarios. To maintain the longevity of these diesel engines in compact platforms, it is crucial to ensure proper care of the timing belt or chain, keep the Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) system clean, and maintain clear intake paths. Furthermore, careful fueling and consistent filtration are essential for sustaining injector performance, directly impacting the overall durability of the diesel engine. When these maintenance practices are followed, diesel engines, even those with modest power outputs, tend to outlast their gasoline counterparts.
What Hurts Diesel Durability In The Modern Age?
Emissions systems introduce additional components requiring clean fluids and regular maintenance. Neglecting these can complicate diesel vs gas engine life. Precision engineering necessitates high-quality filters and fuel; without them, wear accelerates, obscuring the inherent potential for why do diesels last longer. Short trips prevent optimal operating temperatures, leading to soot and moisture buildup that challenges diesel engine vs gas engine longevity. Matching the engine’s use to its design ensures the inherent which lasts longer diesel or gas advantages are maintained. With consistent and disciplined service, the notion that diesel engines last longer than gas remains achievable.