Key Takeaways
- Diesel is more concentrated and ignites by compression while gasoline is more volatile and uses spark ignition. These traits affect engine performance and fuel use.
- Diesel offers torque and efficiency while gasoline provides speed and smoothness. Diesel suits heavy-duty tasks while gas fits lighter, urban driving.
- Misfuelling damages engines and fuel systems. Putting gas into a diesel vehicle, or vice versa, disrupts the combustion process and can cause corrosion, clogged injectors, and failure of critical components like fuel pumps and filters. Acting fast prevents costly repairs.
- Diesel vehicles cost more but offer better fuel economy and resale value. Urban rules and upkeep may offset gains.
- Elan Fuels offers dependable diesel and gas solutions.
Table of Contents
Difference Between Diesel And Gas
Even though diesel and gasoline may both fuel engines, they’re worlds apart in chemistry, performance, and application. While diesel is thicker, less volatile, and refined for compression ignition, making it ideal for heavy-duty engines, gasoline, on the other hand, is lighter, ignites via spark, and suits high-RPM engines found in most passenger vehicles.
Diesel consists of heavier hydrocarbons and is refined at higher boiling points, making it less volatile and suitable for compression ignition. Gasoline rather contains lighter hydrocarbons and is refined for volatility, enabling spark ignition. These chemical differences influence combustion behavior, engine design, and overall performance across various vehicle and equipment types.
Diesel has a higher energy density and lower volatility, igniting under pressure without a spark. Gasoline is more volatile, with lower energy content, and relies on spark ignition. These traits make diesel ideal for long-distance efficiency and heavy loads, while gasoline excels in quick acceleration and responsive urban driving.
Truckers often prefer diesel for the torque it provides when hauling heavy loads. Diesel is commonly used in trucks, buses, generators, and industrial machinery due to its torque and fuel efficiency under heavy loads while gasoline powers most passenger cars, motorcycles, and light-duty vehicles, offering smoother performance and quicker starts that are ideal for everyday commuting and lighter, high-speed applications.
Diesel ignites via compression and delivers higher energy density, making it ideal for trucks, generators, and long-distance driving. It emits more nitrogen oxides. Gasoline, which ignites by spark, is better suited for lighter vehicles and city driving, offering smoother acceleration and lower upfront costs.
Diesel engines deliver fuel economy, ideal for long-haul use, but emit more nitrogen oxides. Gasoline engines offer smoother, quieter rides with lower upfront costs, though they produce more carbon dioxide. Diesel produces more carbon dioxide per gallon burned. Consumer preferences vary too. While diesel is popular in Europe, gasoline dominates in North America due to cost and comfort.
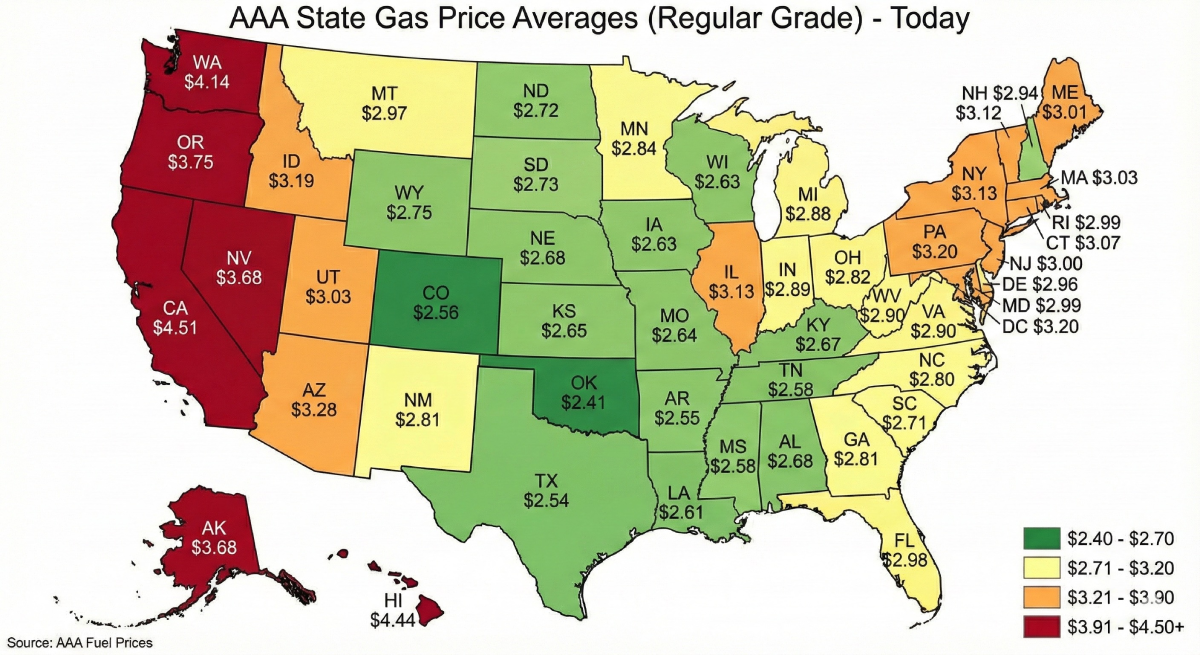
Octane and cetane ratings are key indicators of fuel performance. Octane ratings in gasoline affect engine knock resistance, while cetane ratings in diesel impact ignition quality and cold starts. Diesel prevails in industrial sectors and developing markets, while gasoline suits light vehicles. Fuel prices shift with crude costs and demand, shaping regional trends and vehicle design worldwide.
Diesel Engine Vs Gas Engine
Do all roads really lead to Rome? Diesel engines function using higher compression ratios. In these ratios, air is compressed until it reaches a temperature that is high enough to ignite the fuel and then it is injected directly into the combustion chamber. This method eliminates the need for spark plugs and it results in more efficient combustion. Gasoline engines, on the contrary, mostly rely on spark ignition and operate at lower compression ratios. While this makes them more responsive and quicker to accelerate, it also means they burn fuel less efficiently, especially under heavy loads or long-distance conditions.
In terms of performance, diesel engines excel at delivering high torque at low RPMs(Revolutions per Minute), making them ideal for tasks that require pulling power such as hauling, towing, and industrial machinery. Gasoline engines, however, thrive at higher RPMs. They offer smoother acceleration and better responsiveness for city driving, commuting, and performance vehicles like sports cars. The difference in the torque curves and power delivery makes each engine type suited to distinct driving environments and vehicle roles.
In heavy-duty sectors such as logistics, agriculture, and construction diesel engines are favored for their durability, fuel economy, and long-term reliability. Light-duty sectors, including passenger cars and motorcycles, lean toward gasoline for its lower upfront cost and ease of maintenance. Hybrid diesel-electric models have recently begun appearing in commercial fleets, thereby offering a balance between power and efficiency while reducing emissions and fuel consumption.
Unsure If Diesel or Gas Is Right for You?
Choosing the wrong fuel can cost more than just money—it can cost your engine. Compare diesel vs. gasoline based on your driving habits, fuel costs, and long-term maintenance needs.
Diesel Fuel Vs Regular Gas
Why does diesel not combust properly in gasoline engines? Because it requires high compression and auto-ignition, not a spark plug ignition system. This can lead to stalling, thick smoke, and serious damage to spark plugs, fuel injectors, and the overall fuel system. Since diesel is heavier and less volatile, it disrupts the combustion process in spark-ignition engines. If misfuelling occurs, do not start the engine. Instead, have the tank drained immediately and consult a qualified mechanic to avoid long-term damage and costly repairs.
Insurance policies often exclude misfuelling-related damage, and manufacturer warranties may be voided if the wrong fuel is used. That’s why prevention is critical. Always check pump labels and nozzle size before refueling. Diesel nozzles are typically larger to help prevent mistakes. Staying alert and attentive at the pump not only protects your engine from costly damage but also helps preserve your warranty and avoid unexpected out-of-pocket expenses.
What Happens If You Put Diesel In A Gas Engine?
Is this another situation of trying to fit a square peg in a round hole? Diesel doesn’t combust correctly in gasoline engines due to its heavier composition and lower volatility. When mistakenly pumped into a gas-powered vehicle, it can cause stalling, thick smoke, rough idling, and serious damage to spark plugs, fuel injectors, and the entire fuel system.
Because diesel requires compression ignition, it disrupts the spark-based combustion process in gasoline engines. If misfuelling occurs, do not start the engine under any circumstances. Instead, have the fuel tank drained immediately and consult a qualified mechanic to minimize long-term damage and avoid costly repairs.
Misfuelling is often excluded from insurance coverage and can void manufacturer warranties, leaving drivers with steep out-of-pocket expenses. And so, prevention is key. Always check pump labels and nozzle size before refueling. Diesel nozzles are typically wider to help prevent mistakes. Taking a few extra seconds at the pump can protect your engine, your warranty, and your wallet.
Accidentally Put Diesel in a Gas Engine? Act Fast.
Misfuelling can cause serious engine damage—but quick action can save you thousands. Follow our step-by-step guide to safely handle diesel-gas mistakes.
What Happens If You Put Gasoline In A Diesel Engine?
This is a risky feat. Putting gasoline into a diesel engine can cause catastrophic damage due to the fundamental differences in how each fuel behaves. Gasoline lacks the lubricating properties of diesel, which leads to increased friction and overheating of critical components like fuel pumps and injectors. It can also cause premature wear inside the engine and may prevent it from starting altogether. Even a small amount of gasoline can compromise the entire fuel system.
Always be ready to mitigate the situation if it escalates. If misfuelling occurs, stop immediately and avoid turning on the ignition, as this can circulate the fuel and worsen the damage. Contact a professional to drain and flush the system thoroughly. Repairs can be extremely costly, and in many cases, manufacturer warranties won’t cover misfuelling-related damage. Prevention is always the best safeguard. So thread wisely and with caution.

Which Is Better Diesel Or Gas?
Would you choose diesel or gas? Diesel vehicles come with a higher upfront cost due to their robust engine design and specialized components. However, they offer superior fuel economy and longer engine life, making them a smart investment for long-distance drivers and commercial fleets. Gasoline vehicles, on the other hand, are generally more affordable to purchase and maintain, but they tend to consume more fuel over time, especially under heavy use.
Resale value for diesel vehicles is often higher, particularly in industries like logistics and agriculture where durability matters. Still, tightening emissions regulations and urban driving restrictions can reduce diesel’s appeal in certain regions. Choosing between diesel and gasoline depends on your driving habits, budget, and location. Elan Fuels offers the new standard in fuel distribution.
Want Better Fuel Efficiency for Heavy-Duty Use?
Diesel isn’t just for trucks anymore. Learn how diesel engines outperform gasoline for towing, hauling, and fleet savings—especially over long distances.
Why Is Diesel Different Than Petrol?
“Petrol” has always sounded and felt different. But it is the same thing. “Petrol” is the commonly used term for gasoline in regions such as Europe, Asia, and Africa, while “gasoline” is standard in North America. Though they refer to the same fuel, petrol and diesel differ significantly in refining processes, ignition methods, and the engines they power. Diesel is refined for compression ignition and contains heavier hydrocarbons, while petrol is designed for spark ignition and is more volatile.
While petrol engines prioritize speed, responsiveness, and smoother acceleration, diesel engines are built for torque, fuel efficiency, and long-term durability. Regional policies such as emissions regulations, fuel taxation, and environmental incentives, play a major role in shaping consumer preferences, vehicle availability, and fuel adoption across global markets.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Diesel?
While diesel engines offer durability and fuel efficiency, they come with trade-offs such as:
- High Upfront Cost: Diesel vehicles are more expensive due to robust engine construction.
- Complex Emissions Systems: add maintenance complexity and cost.
- Fuel Price & Access: Diesel fuel can be pricier and less available in North America, even though it is often cheaper in Europe due to taxation differences.
- Noise & Vibration: Diesel engines are louder and less refined than their gasoline counterparts.
- Urban Restrictions: Many cities limit or ban diesel vehicles to reduce pollution.
- Costly Maintenance: Specialized parts and fluids drive up long-term service costs.
Is There A Difference Between Diesel And Gas Vehicle Costs?
Diesel vehicles generally have higher upfront costs due to their robust engine design and advanced fuel systems. However, they often deliver better fuel efficiency, especially on highways and under heavy loads, which can lead to long-term savings. Diesel engines typically require less frequent servicing, but when repairs are needed, they can be more expensive due to specialized components and labor.
For commercial fleets, fuel mileage reimbursements often favor diesel because of its superior range and efficiency. In some regions, tax incentives or credits may apply to clean diesel technologies that meet stringent emissions standards. Ultimately, the total cost per mile depends on several factors, including driving habits, fuel prices, vehicle type, and maintenance practices. For high-mileage drivers or businesses, diesel can offer a more economical solution over time..
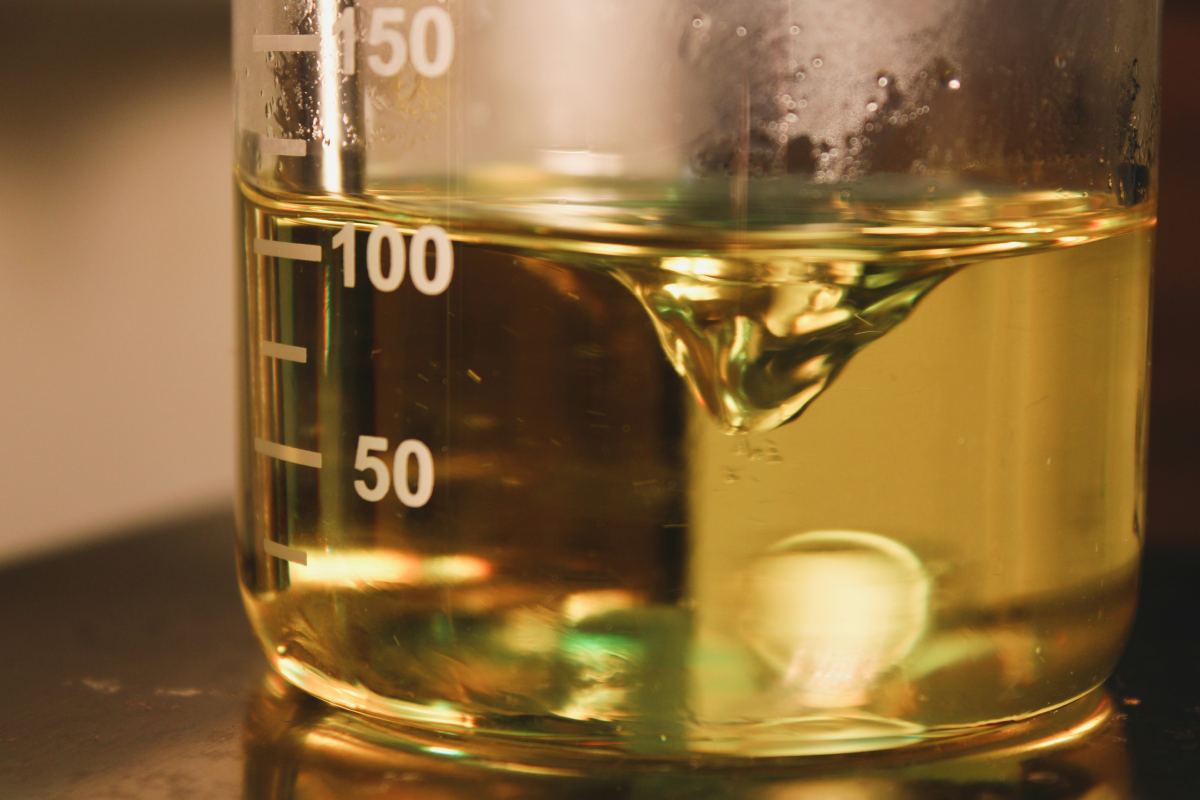
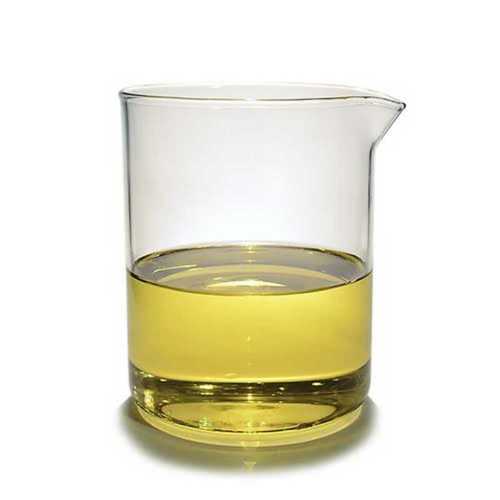
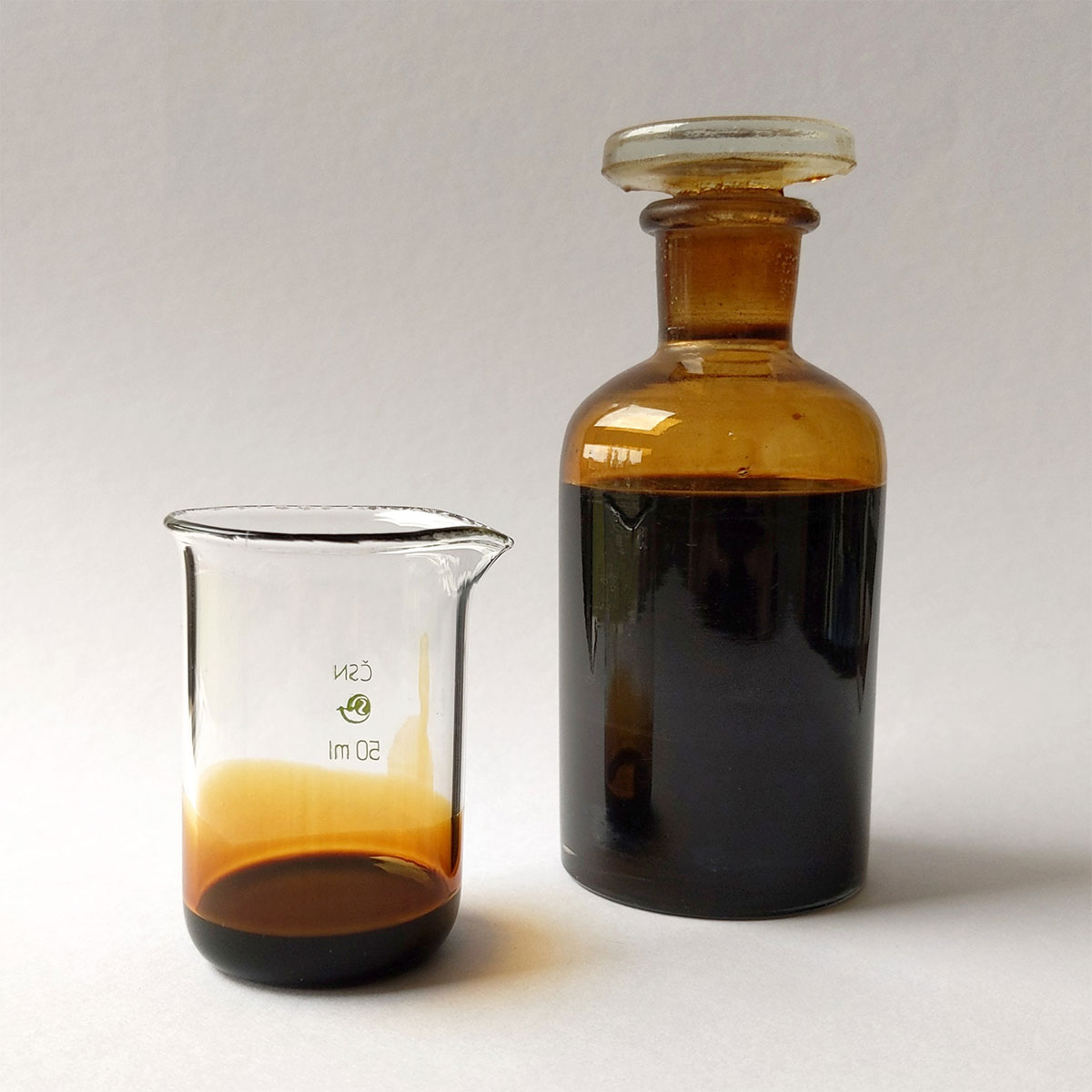
What Color Is Diesel Fuel?
Have you ever wondered what diesel fuel looks like? Diesel fuel is often dyed to distinguish its intended use and comply with tax regulations. Clear diesel is taxed and approved for on-road vehicles, while red-dyed diesel is designated for off-road equipment such as tractors, generators, and construction machinery.
Visually, diesel is typically darker than gasoline, and its appearance can indicate quality. High-quality diesel should be clear and free of particles. Cloudiness, discoloration, or visible sediment may signal contamination, water presence, or degradation. Using poor-quality or contaminated diesel can damage fuel injectors, clog filters, and reduce engine performance. Always inspect fuel clarity and source to ensure safe and efficient operation.