Key Takeaways
- DEF in SCR lowers NOx, clearer air, stronger engines, diesel exhaust fluid.
- Quality matters, use def iso 22241 products like bluedef, avoid harmful contamination.
- Consumption is modest, typical def to diesel ratio near one to fifty.
- Know safety, answer is blue def flammable, it is non flammable, safe.
- Plan service, track levels, decide how much def to add before warnings.
Table of Contents
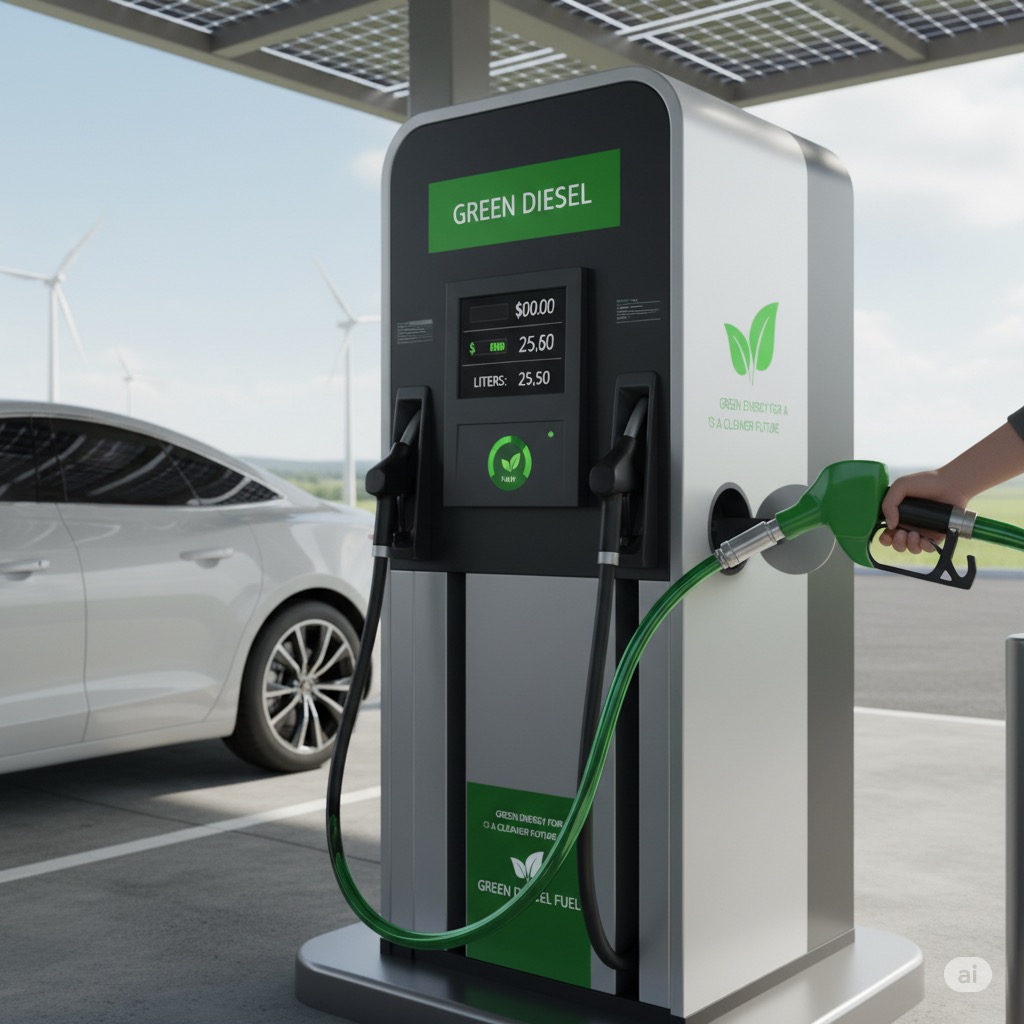
What Is Blue DEF Used For? Understanding Its Purpose In Diesel Engines?
What is blue diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) used for in modern diesels? Blue DEF enables selective catalytic reduction (SCR), which converts nitrogen oxides(NOx) into harmless nitrogen and water. When the exhaust is hot, diesel exhaust fluid supplies ammonia for the catalyst, slashing NOx that harms lungs and limits performance. By keeping emissions low, the system protects aftertreatment hardware and helps avoid costly downtime. Given that dosing is computer controlled, engines can run leaner for power while staying compliant.
Using certified blue diesel exhaust fluid also supports warranty protection, since engines expect DEF iso 22241 quality. Overall benefits are cleaner tailpipes, fewer regeneration events, quieter operation, and steadier torque across loads. That is what bluedef is for, a consumable supporting emissions control, not an optional accessory.
What Is Diesel Exhaust Fluid Used For?
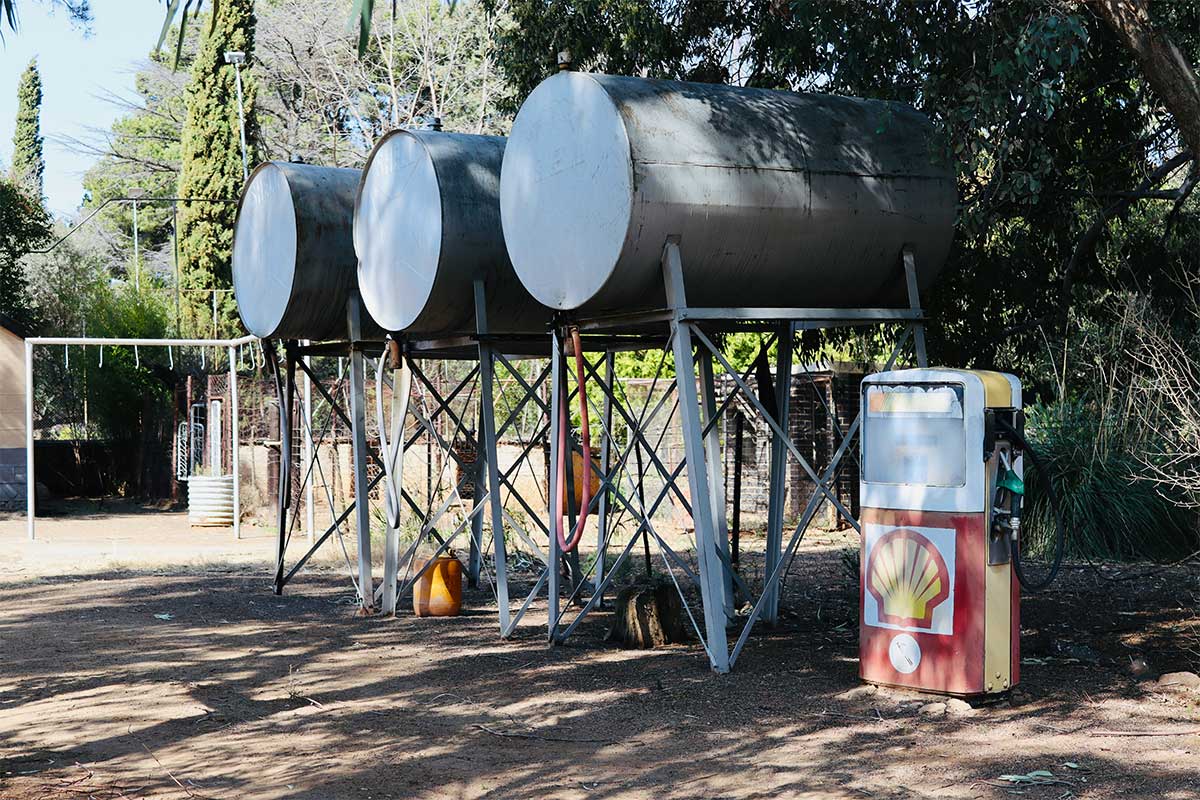
Diesel exhaust fluid is used anywhere SCR equipped diesels operate, that is, in heavy trucks, buses, delivery vans, generators, construction loaders, mining haulers, tractors, and harvesters. It is not burned in the engine, it is injected into the exhaust ahead of the SCR catalyst, where it supports the reaction that converts smog forming NOx into nitrogen and water.
This reaction leads to lower emissions, compliance with clean air rules, and improved public health outcomes in busy corridors. Modern engines calibrate combustion expecting DEF, so overall efficiency and reliability improve when the system is supplied correctly. Cities, farms, and job sites depend on DEF to meet regulations without losing productivity. DEF is valuable beyond long haul routes. It works quietly, automatically and consistently everyday, mile after mile.
Cut NOx, Protect Your Diesel With Certified Blue DEF
Blue DEF feeds your SCR system with ammonia to convert NOx into nitrogen and water, preserving power while staying emissions-compliant. Use DEF that meets ISO 22241 to protect injectors, pumps, and catalysts from deposits and contamination.
What Is Blue DEF Fluid Made Of?
Blue DEF and other brands contain a precise mixture. People ask what is blue def made out of, it is 32.5% high purity urea and 67.5% deionized water. This DEF urea concentration delivers consistent ammonia for SCR and a practical freeze point near 12F. The DEF ISO 22241 standard defines composition, purity, labeling, approved materials, and handling to protect systems. Compliance means low metals, low biuret, and very clean water. Certified packaging minimizes contamination. Using marked products preserves injectors, pumps, catalysts, and supports warranties. For fleet owners or managers, make sure you verify suppliers and batch numbers before accepting deliveries. Quality control and storage discipline are essential for reliability.
Is DEF Fluid Just Salt Water?
DEF is not salt water. It is a specific urea solution blended with purified water that meets DEF ISO 22241 purity limits. Salt ions and many minerals are strictly restricted because they poison catalysts and corrode stainless steel, pumps, and dosing hardware. Adding table salt, tap water, or any unapproved additive pauses risks of crystallization, corrosion, sensor failure, and expensive downtime. Only deionized water and automotive grade urea belong in blue DEF fluid, blended under controlled conditions. If DEF becomes contaminated, the safe action is to drain, flush with certified products, while using correct handling practices. Treat DEF as a precision reagent, not an improvised mix, and your SCR system will remain healthy. Use dedicated funnels, hoses, and closed systems to maintain its purity.
Store DEF Right, Prevent Costly Aftertreatment Damage
Keep DEF sealed, shaded, and cool, and use only approved materials to avoid corrosion and crystallization. Mind shelf life—typically 1 to 2 years—and never substitute water or additives; contamination risks sensors and catalysts.
Is Blue DEF Different Than Regular DEF?
Blue DEF is a Peak brand, peak blue DEF, regular DEF means any product meeting DEF ISO 22241. Comparisons like kleen DEF vs blue DEF mostly show packaging and distribution, not chemistry. Choose sealed, certified containers from suppliers. Prioritize freshness and clean transfer, handling quality counts more than branding.
How Does Diesel Exhaust Fluid Work?
Inside the hot exhaust stream, diesel exhaust fluid vaporizes, urea splits to form ammonia, and the SCR catalyst uses that ammonia to convert NOx into nitrogen and water. The engine control module meters DEF flow precisely so the reaction completes without ammonia overflow. With emissions neutralized downstream, the engines can run efficient combustion for better power and more economy. Reliable DEF quality prevents deposits that can foul catalysts and sensors.
Using the right product therefore protects performance, fuel economy, and compliance at once, delivering cleaner air for communities and dependable torque for work. The process is continuous during operation, invisible to everyone, and coordinated with regeneration events for particulate filters, keeping aftertreatment systems balanced, durable, and ready for demanding duty cycles.
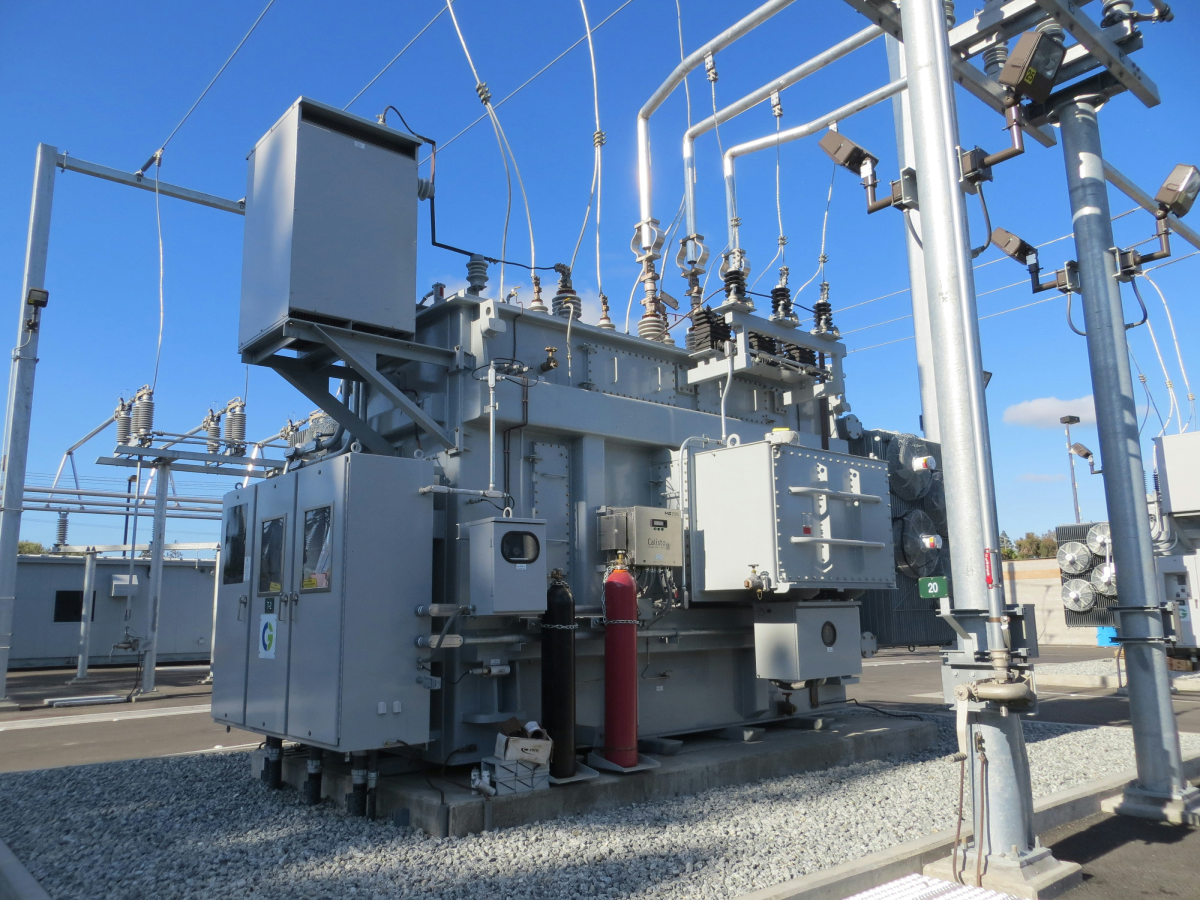
How Does A DEF System Work?
This table breaks down how a DEF system works.
| Component | Role in the SCR system | Inputs and Controls | Key operating notes | Maintenance Checks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEF tank and heater | Stores fluid and thaws it for dosing | Level and temperature sensors feed the control | DEF freezes near 12F and thaws without damage. | Keep sealed, avoid contamination, verify caps and strainers and log batch dayes |
| Supply module and pump | Draws and meters are fluid toward the injector | Commanded by the control module using load and NOx atomization | Filters protect valves and steady pressure enables fine atomization | Replace filters on schedule, check for leaks and cavitation Purge air |
| Heated lines | Carry fluid from tank to injector | Temperature monitored to prevent ice blockages | Lines are insulated and routed away from the heat and sharp bends | Inspect routing, clamps and insulation.Confirm heat function in cold |
| DEF Injector | Sprays DEF into hot exhaust ahead of the catalyst | Pulse width set by the control module using NOx and temperature | Fine spray promotes quick urea decomposition and mixing | Watch for crystallization clean or replace if flow is low Fix faults |
| Upstream and downstream NOx sensors | Measure NOx before and after the catalyst | Feedback trims dosing to hit targets | Faults trigger warnings and derate logic if not corrected | Scan codes, verify readings and replace aging sensor proactively |
| SCR Catalyst | Converts NOx to nitrogen and water with ammonia | Needs proper exhaust temperature and correct dosing | Catalyst materials have defined temperature windows | Keep DEF pure, avoid oil and metalsImmediately address deposits as soon as you notice them |
| Control module and software | Calculate the DEF rate and manage warnings | Use load, speed temperature and NOx signals | New guidance allows staged derate to avoid sudden slowdowns | Keep software current, verify calibrations and document updates |

Is Blue DEF Flammable?
Is blue DEF flammable, no it isn’t. DEF is classified non flammable and non explosive by multiple safety data sheets and carries zero on common fire hazard scales. It is also non toxic under normal use. However, basic precautions in handling still apply;
- Avoid contact with incompatible metals
- Keep containers closed, and rinse spills with water.
- If DEF freezes, let it thaw naturally and do not add additives
- Use only dedicated transfer equipment to prevent contamination.
- Store away from direct sun and strong oxidizers, then recycle or dispose according to local rules.
- Do not mix with fuel, oil, or coolant, and never ingest.
Always check product labels, consult the diesel exhaust fluid safe data sheet for guidance and storage limits, then train staff on handling and first aid.
Does DEF Expire?
DEF does expire. Typical shelf life is one to two years when stored cool and sealed, but it is shorter when temperatures are consistently high. Heat and sunlight accelerate decomposition that raises alkalinity and forms byproducts, risking deposits, sensor faults, and catalyst damage. Labels include manufacture dates so you can rotate stock.
Freezing around 1F does not ruin DEF, tanks and systems are designed to thaw and resume dosing. If DEF smells strongly of ammonia or tests out of the known specifics, replace it. Use certified suppliers and shaded storage to keep quality within DEF ISO 22241 limits throughout the year. In warm regions, plan quicker turnover, purchase smaller containers, or use refrigerated rooms, then regular test to confirm concentration and purity before fleet wide distribution.
Plan Refills To Avoid Power Derate
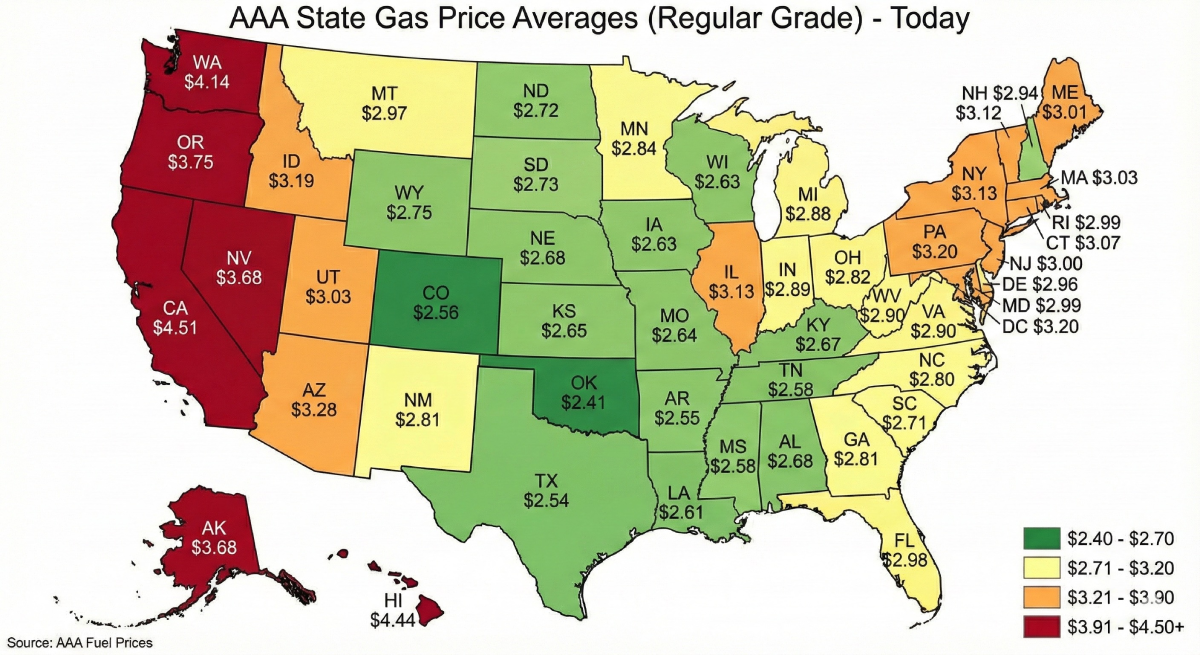
Most diesels use about 2–3% DEF relative to fuel, roughly one gallon per fifty gallons of diesel. Top up before warnings and keep sealed jugs on hand so your truck never hits reduced-power mode.
How Should You Store And Handle DEF?
Proper storing and handling of DEF involves;
- Storing DEF in a cool, shaded place, and keeping it sealed to prevent contamination and evaporation.
- Keep away from direct sun and avoid temperatures above 75F for long periods.
- Use only compatible materials like stainless steel and approved plastics, avoid copper, brass, carbon steel, and zinc.
- Dedicated pumps, totes, and spouts prevent mix ups and keep dust out. Label and log lot numbers.
- If DEF becomes contaminated with fuel, oil, or tap water, do not use it, drain and flush with certified product.
- Let frozen DEF thaw naturally, systems are designed to manage it safely during operation.
Make sure to train drivers and staff in handling, sampling, and spill response, then review suppliers and storage locations to verify DEF ISO 22241 compliance across the operation.
Will DEF Fluid Kill Grass Or Weeds?
Small DEF spills may brown grass from concentrated nitrogen and alkalinity. It is not a weed killer, will DEF kill weeds, no. It is for engines, not soils. Rinse spills with water, avoid runoff to drains, dispose correctly, protect landscapes, use caution. Do not apply as DEF as fertilizer.
How Often Do You Need To Refill DEF?
Most vehicles use DEF at roughly 2-3% of diesel consumption, about one gallon per fifty gallons of fuel. Light duty trucks may go hundreds of miles per gallon of DEF, while heavy vocational cycles consume more. Dashboard indicators show level, range, and warning stages, with final messages prompting refill.
Refilling is simple, open the blue capped port and pour from sealed jugs. For fleet managers, plan inventory using fleet fuel burn, duty cycles, routes, then schedule deliveries before low warnings occur. Many fleets standardize service intervals, topping DEF at oil changes, inspecting caps, screens, and filters. Using certified blue DEF fluid helps maintain consumption and protects sensors, injectors, and catalysts from deposits that may alter dosing rates and trigger faults.
How Much Blue DEF Should You Add?
Add DEF based on consumption, not guesswork. Target the typical DEF to diesel ratio near one gallon for every fifty gallons of fuel. Top the DEF tank whenever you refuel or at scheduled services. Fleets use telematics and fuel burn data to plan deliveries so tanks never reach critical warnings.
What Happens If You Run Out Of Diesel Exhaust Fluid While Driving?
If the DEF tank runs empty, most vehicles enter reduced power mode, then may limit speed severely or refuse to restart until DEF is added. Multiple warnings appear long before this point, so treat them seriously and refill promptly. These behaviors are built in to uphold emissions rules and protect hardware. Refilling with certified blue DEF fluid and cycling the ignition often clears the restriction quickly.
Persistent faults require scanning for codes and addressing sensors, pumps, lines, or crystallized deposits. For safety, plan convenient access to DEF across routes, keep spare sealed jugs in maintenance bays, and train drivers to respond early. This prevents roadside delays, towing, and missed deliveries while keeping air quality improvements on track for communities.
Can You Run A Diesel Without DEF?
Running a modern SCR diesel without DEF is neither practical nor lawful. Software strategies will reduce power and may immobilize the vehicle until the tank is refilled. Bypassing or deleting emissions controls violates the Clean Air Act for on road vehicles and can trigger penalties. It also risks engine and aftertreatment damage, warranty denial, and failed inspections.
Operate as designed, use compliant diesel exhaust fluid, and maintain the system so engines deliver performance with clean air, meeting regulations and customer expectations. Nonroad equipment also falls under tampering prohibitions in many jurisdictions. Fleets set policies against alterations, audit shops for compliance, and train drivers to log low DEF alerts so maintenance can respond before derate conditions impact schedules, safety, and efficiency.
What Happens If You Put Water Instead Of DEF?
Water is not a substitute for DEF. Without urea, the catalyst receives no ammonia, NOx reduction fails, and the system will set fault codes and likely derate. Tap water introduces minerals that corrode components and poison catalysts. Even deionized water alone is wrong, because concentration matters for freeze point and chemistry. If water enters the tank, drain, flush with certified product, repair damage, and recalibrate as required. Never dilute blue DEF fluid to stretch supply. Sensors are calibrated to expect the precise 32.5% concentration defined by DEF ISO 22241, and dosing maps rely on that chemistry to avoid ammonia slip. Make sure you protect your system by using sealed containers, closed dispensing, and trained staff only.
Can You Make Your Own DEF Fluid?
Do not make DIY DEF. Blending urea and deionized water at home cannot meet DEF ISO 22241 purity, leaving contaminants that damage pumps, injectors, and catalysts. Non-compliant fluid risks fines and downtime. Buy certified blue DEF or equivalent from suppliers, and verify batch dates and seals on delivery.
Can Pee Replace DEF?
No, urine cannot replace DEF. Automotive DEF contains high purity urea in deionized water to protect catalysts and sensors. Human urine is dilute, variable, and contaminated with salts and organics that corrode and poison SCR systems. Use only certified products that meet DEF ISO 22241, never use improvised substitutes or myths.