Key Takeaways
- Diesel energy density supports range and fewer fuel stops under load.
- Low rpm torque explains why trucks use diesel for towing.
- Robust construction improves longevity and uptime for fleets.
- Aftertreatment manages emissions while keeping efficiency high.
- Misfueling with gasoline risks pump and injector damage.
Table of Contents
Why Do Trucks Use Diesel?
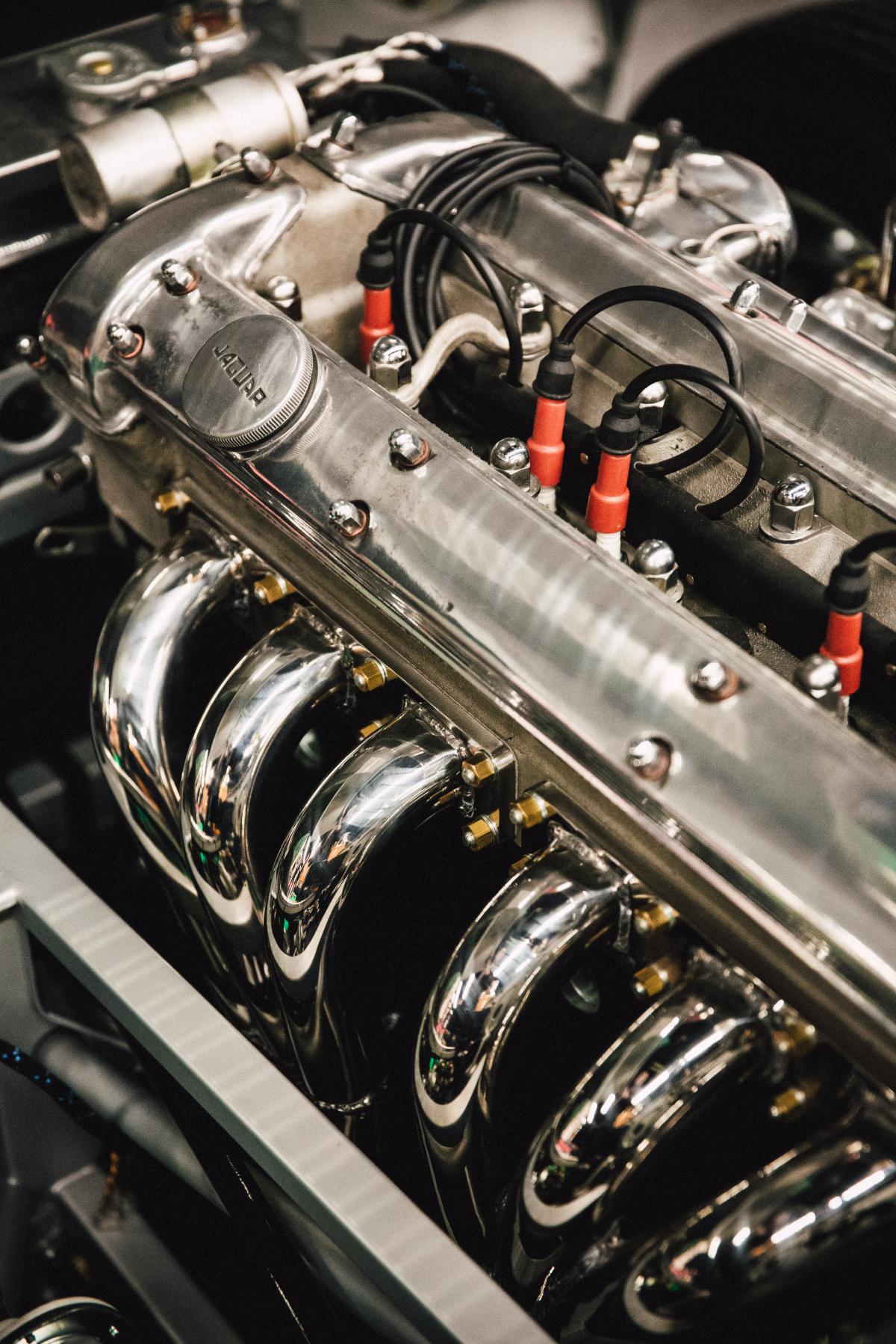
Trucks rely on diesel primarily due to compression ignition, higher brake thermal efficiency, and strong torque. This is why you’ll find that Class 4-Class 8 vehicles, especially semitrucks used for long hauls, depend on diesel for its range and durability. While some light duty exceptions exist, the need for continuous operation largely explains why trucks use diesel fuel.
These factors also clarify why a semitruck uses diesel fuel and not gasoline, and why trucks use diesel instead of gas or petrol. Ultimately, the demanding duty cycles of heavy vehicles confirm that diesel is the preferred choice over petrol for such applications.
Greater Fuel Efficiency And Energy Density?
Trucks frequently use diesel because it offers greater energy per unit volume compared to gasoline, which is excellent for achieving long ranges and maintaining stable highway economy. This translates to lower specific fuel consumption, leading to reduced overall fuel purchases over time. These factors help explain why trucks use diesel for cost per mile and why a semitruck would use diesel fuel and not gasoline, or why trucks use diesel instead of gas or instead of petrol.
The same principles clarify why diesel is used in heavy vehicles instead of petrol and confirm that trucks do use diesel for freight transport. To discover potential savings for your fleet, consider asking for a free Fleet Fuel Cost Review, which can map out savings based on routes, idle rules, and schedules.
Cut Diesel Cost Per Mile
Modern diesel engines shine on long routes. Get a quick cost-per-mile snapshot using your MPG, routes, and idle patterns to see where diesel efficiency pays off for your fleet.
Higher Torque For Heavy Loads?
Torque refers to the pulling force at the wheels. Turbocharged, high-compression designs are excellent at delivering strong low rpm torque. This is precisely why semis use diesel for their gradeability and to launch with a full payload. It also explains why trucks use diesel fuel when towing and why a semi-truck would use diesel fuel and not gasoline. This clarifies why trucks use diesel instead of gas, why trucks use diesel instead of petrol, and why diesel is used in heavy vehicles instead of petrol, ultimately demonstrating that trucks use diesel for heavy work.
Engine Longevity And Durability?
Trucks, particularly semi-trucks and other heavy vehicles, primarily use diesel fuel instead of gasoline or petrol. This choice is due to several key factors that contribute to their longevity and operational efficiency. Diesel engines often feature stout blocks and forged internals, which enhance their durability. They also benefit from high-capacity cooling systems and operate at lower cruising RPMs, all of which extend their service life and maximize uptime. These characteristics explain why trucks use diesel fuel for long service intervals, making it clear why diesel is used in heavy vehicles instead of petrol, and confirming that trucks do use diesel.
Diesel Vs Gasoline Engines In Trucks And Trailers?
The fundamental difference lies in their ignition systems and performance characteristics. Gasoline engines use spark ignition and typically achieve peak power at higher revolutions per minute. Diesel engines, on the other hand, utilize compression ignition, delivering strong low rpm torque and better fuel efficiency, especially when operating under a heavy load.
These distinctions explain why trucks use diesel. For tasks involving light duty and short city cycles, gasoline can be suitable. However, for heavy trailers and long highway journeys, the robust torque and superior efficiency of diesel are highly advantageous. This clarifies why semis use diesel instead of gas or petrol, making diesel the preferred choice for heavy vehicles.
How Diesel Engines Work
Trucks, including semi-trucks, use diesel fuel because it’s a highly efficient and controlled process. Air is first compressed until it’s hot, then fuel is injected, and the charge self-ignites. To further enhance this, turbocharging and intercooling increase the mass of air, while common-rail systems ensure precise fuel injection timing. This mechanism explains why trucks use diesel fuel and why trucks use diesel instead of gas or petrol, especially in heavy vehicles, confirming that trucks do indeed use diesel.
How Gasoline Engines Work
Gasoline engines mix air and fuel, which is then compressed and ignited by a spark plug. Their performance is characterized by high RPM power and sensitivity to octane levels. This clarifies why diesel is preferred for heavy vehicles like trucks and semi-trucks, especially when hauling significant loads, as opposed to gasoline or petrol. This explains the common use of diesel in heavy vehicles and trucks, and why semi-trucks specifically rely on diesel for freight transport.
What Are The Downsides Of Diesel Engines?
While trucks using diesel can come with a higher purchase price, heavier components, and more complex aftertreatment systems, these added costs are often offset by the benefits. Drivers might also have concerns about noise and smell, which are valid points to consider. However, these tradeoffs don’t eliminate the fundamental reasons why trucks use diesel, particularly when it comes to ensuring consistent uptime and reliability for demanding routes.
These factors help to explain why a semi-truck would use diesel fuel and not gasoline, and why trucks use diesel instead of gas or instead of petrol. Ultimately, they confirm why diesel is used in heavy vehicles instead of petrol, and clarify that trucks do use diesel for their most challenging and rigorous tasks, where power, efficiency, and durability are paramount.
Match Torque To Your Load
Diesel’s low-RPM torque is built for towing and grades. Enter trailer weight and route profile to verify you have the pulling power and gearing you need before the next haul.
Environmental Considerations
Diesel engines are the backbone of the trucking industry, powering the massive vehicles that transport goods across vast distances. Their robust design and specific fuel requirements make them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Here’s a look into why diesel is the fuel of choice for trucks, highlighting its efficiency, power, and compatibility with modern emissions controls.
| Reason for Diesel Use in Trucks | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Modern Emissions Systems | Ultra-low sulfur diesel supports modern emissions systems like Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) to cut NOx and Diesel Particulate Filters (DPFs) to trap soot. These controls help maintain efficiency. |
| Efficiency | The inherent efficiency of diesel engines is a primary reason why trucks and semi-trucks utilize diesel fuel. |
| Power for Heavy Vehicles | Diesel engines are known for their high torque output, which is crucial for moving heavy loads and maintaining power over long distances, explaining why diesel is used in heavy vehicles instead of petrol. |
| Fuel Type Confirmation | Trucks do use diesel, and specifically diesel fuel, for the reasons mentioned above. |
What Is The Worst Thing For A Diesel Engine?
Several factors contribute to engine damage and the rationale behind diesel use in heavy vehicles. These considerations highlight the importance of proper maintenance and fuel type:
- Poor maintenance
- Contaminated fuel
- Lots of short trips
- Ignoring regenerations
- Accidental gasoline in a diesel engine (reduces lubrication, damages pumps and injectors)

Diesel Fuel Explained
Diesel is a denser distillate fuel compared to gasoline. Its cetane rating indicates ignition quality, while lubricity impacts pump wear. Cold flow properties and sulfur content are critical for reliability and aftertreatment systems. These characteristics collectively explain why diesel, rather than gasoline or petrol, is the fuel of choice for trucks, semitrucks, and other heavy vehicles.
Uses Of Diesel
Diesel’s torque and economy make it indispensable for trucking, agriculture, construction, marine, and rail. Similarly, stationary generators rely on diesel for its extended runtimes and efficiency. These applications highlight why diesel is the preferred fuel for trucks, especially semi-trucks for line haul, and explain its widespread use in heavy vehicles over gasoline or petrol.
Should I Buy A Diesel Truck As A Daily Driver?
When choosing between diesel and gasoline for your truck, consider your typical usage. Diesel is the preferred choice if you frequently tow, haul heavy loads, or drive long distances. This explains why do trucks use diesel and why do semis use diesel for heavy-duty applications. It also clarifies why would a semitruck use diesel fuel and not gasoline, why do trucks use diesel instead of gas, and why do trucks use diesel instead of petrol, as well as why diesel is used in heavy vehicles instead of petrol. Essentially, for demanding work needs, do trucks use diesel due to its superior torque and fuel efficiency under load. On the other hand, gasoline is generally better suited for short trips, lighter loads, and offers a lower upfront cost.
Protect Your Diesel Engine
Avoid misfueling, skipped regens, and contamination. Download a one-page checklist that covers SCR/DPF care, fuel quality, cold-flow prep, and injector protection.
Is It Cheaper To Drive Diesel Or Gas?
The cost per mile for a truck depends on several factors, including fuel price, miles per gallon (mpg), the load being carried, and the route taken. When it comes to steady highway duty, trucks typically use diesel, and semis also commonly use diesel for long hauls. This is because diesel often offers advantages for these types of driving conditions. You might wonder why trucks use diesel instead of gas, or why trucks use diesel instead of petrol, and ultimately, why diesel is used in heavy vehicles instead of petrol. While highway hauling generally favors diesel, city driving cycles might make gasoline a more suitable option. So, why would a semitruck use diesel fuel and not gasoline? Ultimately, most trucks do use diesel.
Which Type Of Engine Lasts Longer?
Diesel engines are often preferred for heavy-duty applications because their design and lubrication allow them to last longer under strenuous use. Of course, proper maintenance is crucial for any vehicle, regardless of its power source. This explains why do trucks use diesel and why do semis use diesel. It also addresses why do trucks use diesel instead of gas and why do trucks use diesel instead of petrol, as well as why diesel is used in heavy vehicles instead of petrol. Essentially, for demanding work, trucks do use diesel, and it’s clear why do trucks use diesel fuel.
Do Some Trucks Still Use Gasoline?
Yes, many light-duty pickups and some medium-duty vehicles still use gasoline. This is often due to a lower initial purchase price and their primary use in city driving. This distinction helps explain why trucks use diesel in heavier applications and why trucks use diesel when significant loads are involved. It also clarifies why semis use diesel, why a semitruck would use diesel fuel and not gasoline, why trucks use diesel instead of gas, why trucks use diesel instead of petrol, and why diesel is used in heavy vehicles instead of petrol.