Key Takeaways
- Diesel vs. heating oil looks similar, but additives, taxes, and intended equipment use can vary significantly.
- Diesel fuel vs heating oil can work in some heating systems in emergencies, but you should follow safety limits.
- Heating oil and diesel fuel pricing often differ due to road taxes, retail demand, and distribution patterns.
- The differences between fuel oil and diesel matter most for legality, storage, and engine protection.
- The difference between heating oil and diesel depends on what you mean, as they are chemically similar, but legally and operationally not always the same.
Table of Contents
Heating Oil Vs Diesel
When people say they are basically the same thing, they usually mean the base fuel is a middle distillate. That can be true, but practical differences still exist
Heating fuel for homes is typically purchased and delivered in bulk, whereas road diesel is available through more retail channels. The price of road diesel often includes additional tax and compliance costs, which can increase the overall cost. The equipment and usage also differ significantly; for example, home heating systems burn fuel in a controlled burner and heat exchanger, while engines inject fuel at high pressure, demanding tight control over lubricity, cleanliness, and combustion timing. This difference in application is why the question of diesel vs home heating oil is not a simple one, varying significantly from one furnace system to another. Some heating fuels are dyed in many regions to show they are not taxed for on-road use. This is one reason people ask is heating oil diesel fuel and get mixed answers.
While viscosity, ignition quality, and stability are fundamental properties common to both diesel and heating fuel, their specific additive treatments and handling procedures diverge significantly. Diesel fuel is often prioritized for enhancements related to cold flow operability, maintaining injector cleanliness, and compatibility with modern emissions control systems. Conversely, heating fuel treatments typically focus on long-term storage stability and optimal burner performance. These distinct choices in formulation directly impact factors such as ignition behavior, the propensity for soot formation, the risk of filter plugging, and necessary maintenance intervals for equipment.
Difference Between Home Heating Oil Vs Diesel
A frequent point of comparison is home heating oil vs. diesel, as both are classified as number 2 grade fuels. While they share similarities in boiling range and energy content, they are manufactured and distributed for distinct applications. Both are petroleum-based middle distillates and can combust effectively under proper burner conditions, which is why emergency substitution may be feasible in some cases. The key distinctions that show up in real use as follows;
- Diesel for engines is usually managed to meet engine performance needs, such as deposit control, lubricity, and consistent combustion quality.
- Home heating fuel is usually managed around burner reliability and long storage periods, especially in seasonal use.
- Legal rules often differ, especially when dyed fuel is involved, which matters for vehicles and inspections.
Unsure If Heating Oil And Diesel Are Interchangeable?
If you are trying to decide between heating oil vs diesel, we will help you match the right fuel to your furnace or equipment, avoid costly mistakes, and understand what “No. 2” really means in real-world use.
Is Heating Oil Actually Diesel Fuel?
The question, is heating oil diesel, arises due to their chemical similarity, as they can overlap in carbon range and energy density. However, legally and commercially, they are often distinct commodities, separated by tax structure, mandated dyeing for heating oil, and differing specifications set by regulators or suppliers.
- Limited substitution is sometimes possible: A furnace designed for No. 2 heating oil can often safely burn regular diesel fuel for a brief emergency period, provided the burner is well-maintained and the fuel is clean.
- Reasons why they are not interchangeable: Using heating fuel in an on-road vehicle is typically illegal if the fuel is dyed or untaxed for road use. Furthermore, it poses a risk to modern, high-precision engines that are highly sensitive to variations in fuel quality and contamination. This complexity is why the answer to is home heating oil diesel is not a simple affirmative for all situations.
What Similarities Do Fuel Oil Vs Diesel Fuel Share?
The reason fuel oil vs diesel keeps coming up is that both fuels often sit in the same broader distillate family. They share similar energy density per litre and similar combustion behaviour in the right type of burner.
Some of their shared characteristics are
- Both can atomise and burn in pressure-type burners when viscosity is in the workable range.
- Both can deliver strong heat output because their energy content is broadly comparable.
- Both can be stored in tanks and delivered by truck using similar handling practices.
A heating burner mainly needs a fuel that will flow, atomise, ignite, and burn steadily. Many diesels meet those needs, especially when temperatures are moderate and the system is maintained. This is why people sometimes use the term ‘diesel heating oil’ casually, even though labels can mask real regulatory and additive differences.
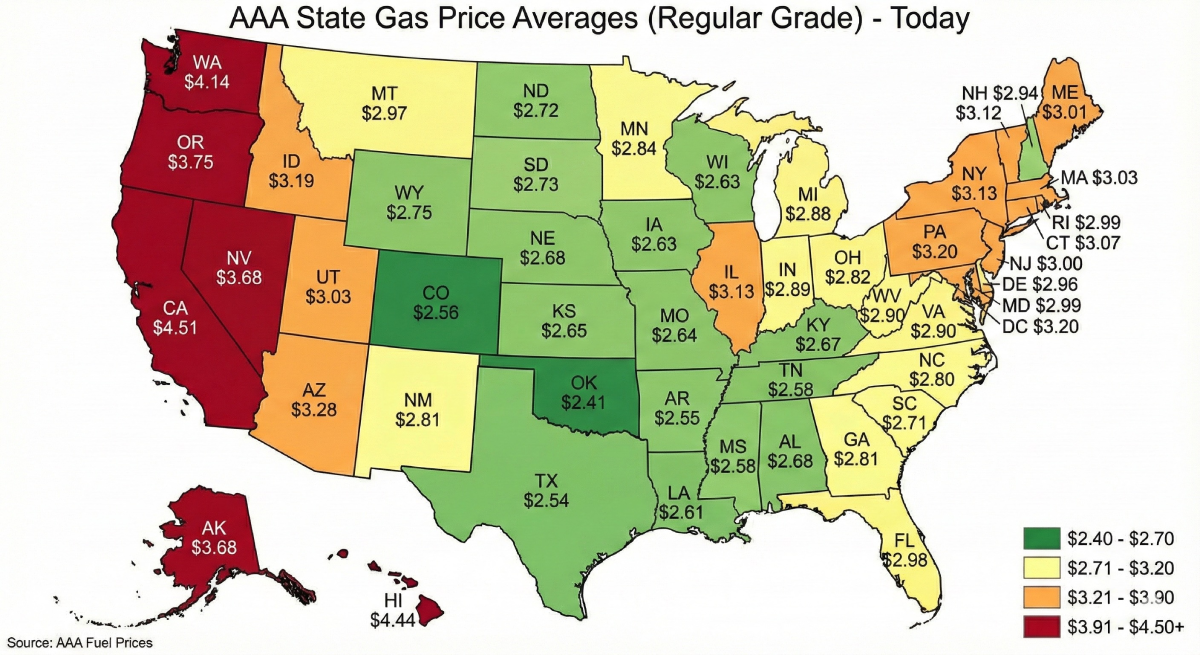
How Do Costs Compare Between Diesel Vs Home Heating Oil?
In many markets, diesel vs home heating oil is more expensive on the diesel side. The biggest drivers are tax, compliance, and where the fuel is sold, as follows;
Road tax and fees can raise diesel prices relative to heating fuel.
- Retail distribution and convenience pricing can add margin to diesel.
- Seasonal heating demand can raise heating fuel prices in winter in some regions.
- Supply chain constraints and refinery maintenance can swing both fuels up or down.
Below is a simple comparison of factors that often push price, not exact numbers.
| Factor | Often affects heating fuel | Often affects diesel |
|---|---|---|
| Road tax and on-road compliance | Lower | Higher |
| Retail station markup | Lower | Higher |
| Winter heating demand | Higher in cold months | Sometimes higher, but less tied to heating |
| Fleet and trucking demand | Lower | Higher |
| Dye programs for off-road use | Common in many regions | Can exist for off-road diesel too |
If you need diesel for your engines, choose a reliable, high-quality supplier. For high-performing engines, you can buy high-quality diesel from us.
This cost discussion is also why people search for ‘diesel vs fuel oil’ and ‘diesel fuel vs fuel oil’ when deciding what to buy for their specific equipment.
Need Heat Tonight And Only Diesel Is Available?
In a true emergency, diesel fuel vs heating oil can sometimes be a temporary workaround for certain No. 2 oil furnaces. We will walk you through the safest limits, clean transfer tips, and warning signs that mean stop and call a technician.
How Storage Requirements Differ For Heating Oil And Diesel
Storage needs for heating oil vs. diesel may overlap, but the details differ by tank location, water control, and cold-weather handling. The key storage practices that matter most are;
Outdoor tanks are subject to greater temperature fluctuations, which elevates the potential for condensation. Indoor tanks generally maintain warmer temperatures, which helps mitigate the risk of fuel gelling but still necessitates clean handling practices. Both standard diesel and heating fuel are susceptible to thickening and flow restriction at low temperatures, with gelling potential depending on the specific blend and any treatments applied. In colder climates, anti-gel additives are often required for both fuel types, particularly for outdoor tanks and systems with long fuel lines. The decision of whether fuel treatment is necessary should be based on local temperature forecasts, the fuel blend in use, and the level of exposure of the tank and piping.
Long-Term Stability And Degradation Rates
Both fuels can degrade over time due to oxidation and contamination. Prolonged storage often leads to the formation of gums and sludge, which can result in filter plugging. Stabilizers are generally more crucial for heating fuel, as it tends to be stored longer during seasonal use. Diesel for equipment that sits idle for extended periods faces comparable degradation issues. The risks associated with this degradation can be mitigated by using clean tanks, maintaining strict water control, and periodically turning over fuel.
Differences Between Heating Fuels, Kerosene, And Diesel Fuel?
Understanding the differences is key when considering furnace oil vs diesel and their potential for blending. Heating fuels are typically engineered for use in boilers and furnaces, while kerosene is a lighter distillate, valued for its better cold flow properties, making it suitable for space heaters, lamps, and blending. Conversely, diesel is specifically formulated with additive packages for optimal performance in compression ignition engines.
In a practical comparison, kerosene generally exhibits lower viscosity and superior cold flow characteristics than many number two heating fuels. While heating fuel and diesel can be quite similar, the final product is always determined by local specifications and the additives used. Modern engines often demand a higher level of refining and cleanliness, which influences fuel expectations. Furthermore, kerosene blends are frequently recommended in very cold conditions to improve flow and mitigate gelling risk in both heating equipment and diesel engines, subject to manufacturer guidance and fuel availability.

Can You Use Diesel Fuel In A Heating Oil Furnace During An Emergency?
In emergency situations, considering diesel fuel vs heating oil offers a temporary solution for restoring heat. It is often acceptable to use diesel in a number two oil furnace when the proper fuel supply is exhausted. This should only be done if you can safely access clean diesel and transfer it to the tank. Ensure your heating system is well-maintained with decent filters and a good nozzle before proceeding. Safety is paramount when handling fuel. Use only clean product to prevent component fouling and subsequent system failure. Prevent spills ventilate the area well and adhere to all local fire safety guidelines. Never mix unknown or random fuels. If the furnace begins to smoke smells strongly or repeatedly cycles off stop immediately and call a qualified technician. This is strictly a temporary measure. Plan for a proper heating fuel delivery and schedule maintenance if the burner performance changes following this emergency event.
Can You Use Heating Oil In A Diesel Engine Or Vehicle?
This is where the risks are highest, which is why oil vs. diesel questions show up in search. People may have heating fuel on hand and wonder if it can power a vehicle. Below are the main risks and issues
- Legality can be a problem if the fuel is dyed or untaxed for road use. That is why people ask is furnace oil is diesel and get warnings.
- Modern diesel engines can be sensitive to fuel cleanliness and stability. Tank sediment or water that is tolerable in a home tank can damage injectors.
- Emissions systems can be affected by off-spec fuel, resulting in costly repairs.
Homeowners also ask if they can use heating oil in a diesel engine during shortages or emergencies. In most cases, it is not worth the legal and mechanical risk. If you are comparing diesel vs oil for an engine, stick with on-spec diesel from a reputable supplier.
Want To Cut Fuel Costs Without Breaking Any Rules?
Diesel vs home heating oil pricing can change because of road taxes, retail markups, and seasonal demand. Learn what actually drives cost in your market, plus smart storage and additive choices that protect burners and reduce headaches.
Should You Use A Heating Oil Additive?
Additives exist to solve real problems such as sludge, oxidation, cold-flow restriction, and burner deposits. Whether you need one depends on storage time, tank condition, and climate. Additives can help in the following situations;
- Long storage periods between deliveries.
- Older tanks may have sediment.
- Repeated filter plugging or unstable burner operation after checking basic maintenance.
- Cold-weather operation where flow issues occur.
The primary concern for fuel treatment in winter is cold flow support. Conversely, in warmer months, the emphasis shifts to stability and cleanliness, particularly if the fuel will be stored for an extended period. Always adhere to the product’s instructions and avoid over-treating the fuel.