Key Takeaways
Table of Contents
What Is Race Fuel?
Race fuel is a specialised fuel engineered for motorsports and other high-performance engine applications. Its formulation is designed to consistently resist engine knock, burn reliably and predictably, and maintain uniform quality from batch to batch. Understanding what racing fuel is and its specific properties is critical when an engine is optimised for high cylinder pressure, such as in high-compression engine builds, turbocharged or supercharged (boosted) engines, or engines utilizing aggressively advanced ignition timing. Key traits of is race gas in motorsports include;
- Higher knock resistance than typical street fuel, linked to race fuel octane and blend quality.
- Better repeatability from drum to drum, which supports tuning and data logging.
- Controlled volatility to match the operating range of the engine and the event.
- Cleaner, more stable storage compared with many seasonal retail blends.
- Use across drag racing, drifting, NASCAR-style stock car series, circuit racing, karting, and time attack, depending on rules and engine design.
In everyday terms, racing gasoline is fuel engineered to help an engine maintain safe power under harsh conditions. When people ask what gas do race cars use, the accurate answer is that it depends on the series, but the goal is always predictable combustion and reliability.
What Actually Is Race Fuel Made Of?
In response to the common question, what is racing fuel made of, the composition typically begins with meticulously selected hydrocarbons. Manufacturers then incorporate additional components to precisely control factors like burn speed, knock resistance, and stability. Some specialized formulas utilize oxygenated components to increase the amount of oxygen available during combustion, while others emphasize exceptionally stable hydrocarbon fractions achieved through premium refining processes.
Compared with typical retail gasoline, high-octane race fuel is formulated to significantly tighter tolerances. This precision is essential for tuners, as it ensures a consistent response when they adjust engine parameters such as timing, boost, and the air-fuel ratio. Ultimately, while it is a fuel, the blending of racing fuel prioritizes consistent, high-level performance over the broader consumer compatibility targeted by standard pump gasoline.
What Is Race Fuel Called In Motorsports?
The name of the race fuel is determined by the specific racing team, the fuel supplier, and the governing body’s rulebook. Common nomenclature includes race gasoline, race car gas, and labels specifying racing gas octane levels. Examples of simple blend names are unleaded 100 or oxygenated 104, depending on the brand. Some series mandate a precise product code, while others define necessary properties like octane rating, oxygen content, and whether the fuel must be unleaded.
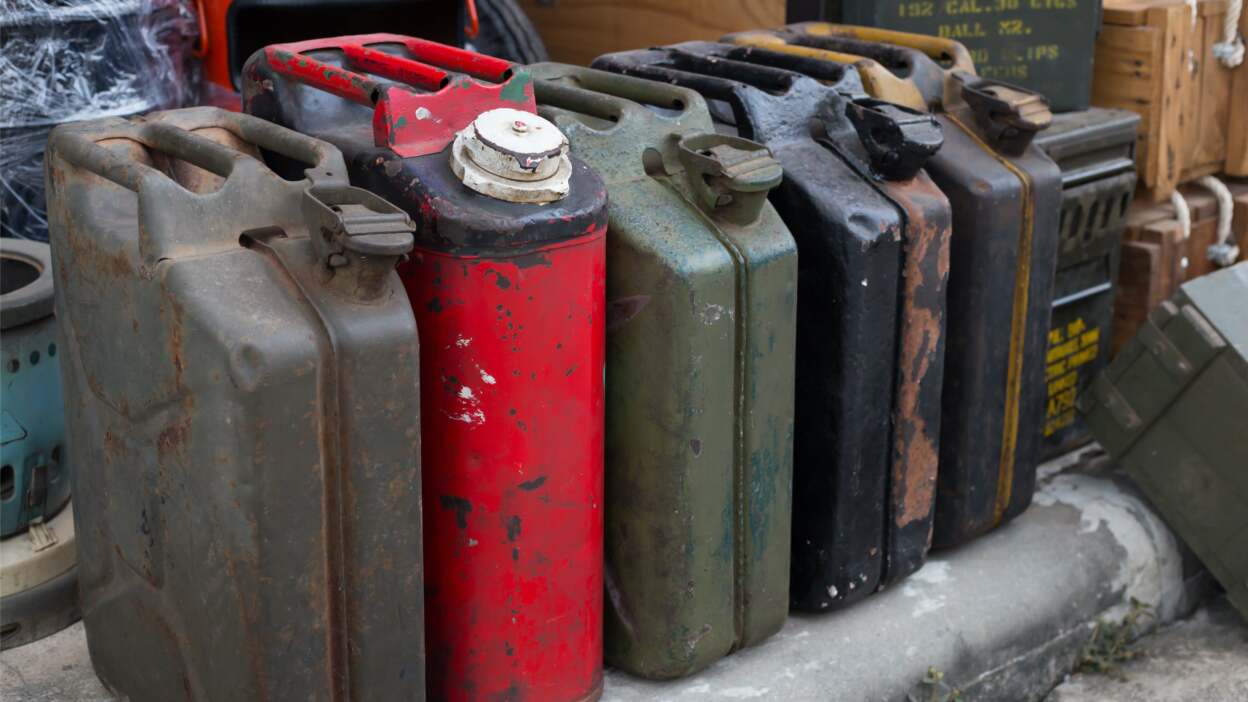
You may also ask what is race gas in terms of its lead content, as it is described as either leaded or unleaded. While leaded fuels offer superior knock resistance, they are incompatible with many modern emissions systems. Unleaded race blends are widely used in classes where modern engine management systems are present. When sourcing fuel, stable quality and clean storage, including the use of proper race gas cans, are essential for optimal engine performance and longevity.
Unsure Which Race Fuel Octane You Actually Need?
If your setup is boosted, high compression, or aggressively timed, the right race fuel octane rating is about knock safety and consistency, not bragging rights. Use this quick checklist to match octane to your build, heat conditions, and tuning goals, so you stop guessing at the pump.
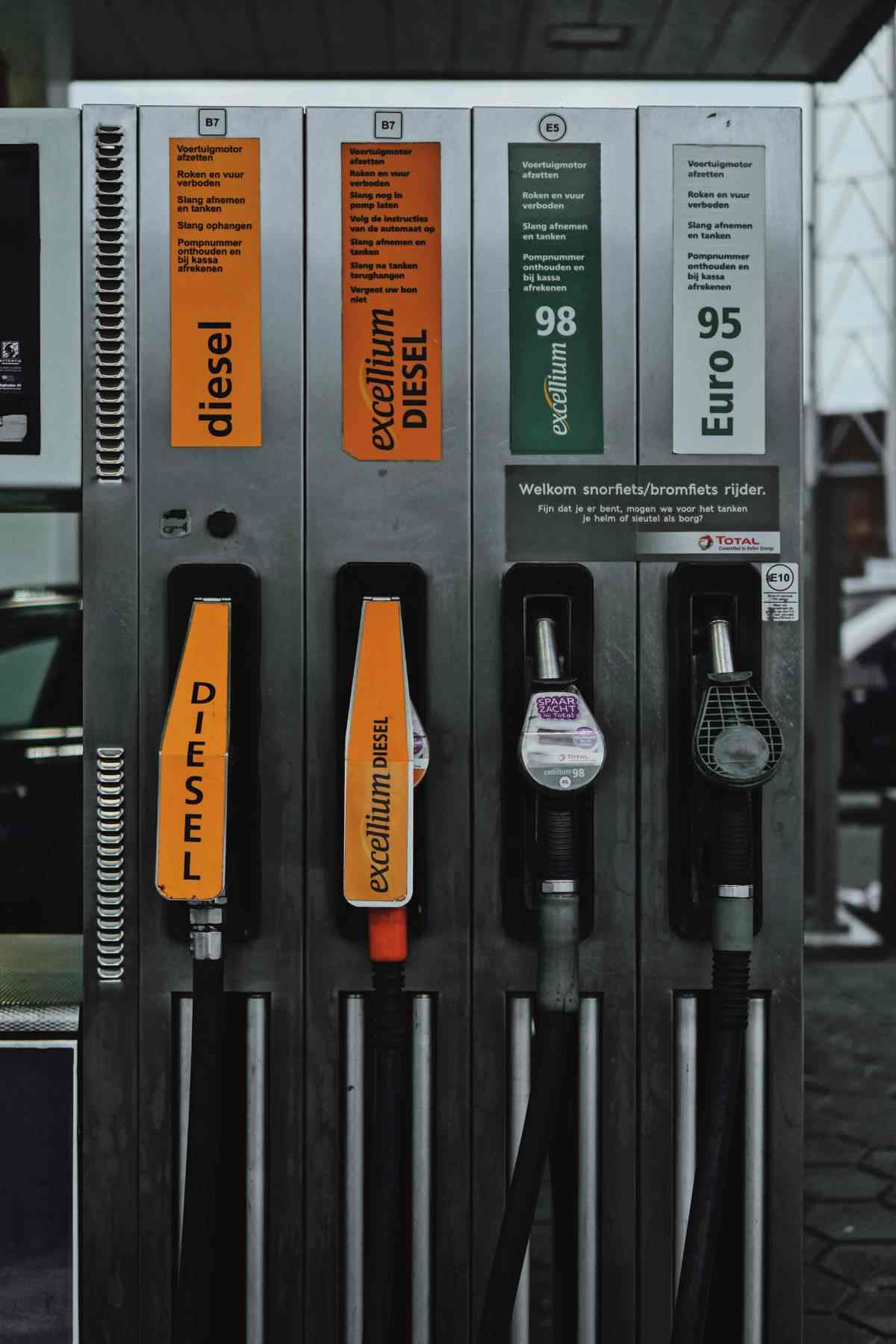
Difference Between Race Gas And Regular Pump Fuel
What is race gas? It is a specialized fuel that differs significantly from retail pump gasoline because it is engineered for a very narrow and specific purpose: maximizing engine performance. Standard pump fuel is formulated to function reliably across millions of diverse vehicles, climatic conditions, and driving styles. In contrast, race blends are precisely designed to achieve controlled combustion right at the limit of an engine’s performance capability. This is why highly tuned engines often require a consistent race fuel octane rating that remains stable and predictable from one refueling to the next.
Here is a simple comparison table showing the differences between many race blends and typical pump fuel.
| Category | Typical pump gasoline | Typical race gasoline |
|---|---|---|
| Consistency | Can vary by season and region | Tighter blending and quality control |
| Knock resistance | Limited to street engine requirements | Higher race gas octane level options |
| Volatility focus | Broad range for everyday drivability | Tuned for specific performance operating ranges |
| Additives | Emissions compliance and deposit control | Performance, stability, and combustion consistency |
| Best use | Daily driving and general road use | High-load, high-performance, and competition use |
A tuned engine may not gain power from race fuel unless the calibration takes advantage of it. But the stability and knock resistance can protect the engine under harsh conditions.
What Separates A Race Fuel From A Street Fuel?
The primary distinction between fuel types is purpose. Race gasoline is precisely engineered for high-pressure combustion, ensuring controlled, stable power through managed volatility and shaped burn characteristics. Conversely, street fuel must accommodate a broader range of constraints, including emissions, cold starts, and fuel economy. Therefore, even high-octane pump gas often does not perform like racing gasoline during continuous wide-open throttle operation.
How Does Race Fuel Differ From Regular Gasoline In Composition?
The technical complexity of what is racing fuel lies in its composition. Specialized blends utilize different hydrocarbon families and advanced refining processes. Some incorporate oxygenated components, which allow for changes in the required fuel-to-air ratio while maintaining airflow. Generally, these fuels are engineered for a stable, high-performance response, even under prolonged, high-stress conditions.
This refined composition is why the discussion around racing fuel octane and race fuel octane is essential. Octane itself does not quantify energy; rather, it measures the fuel’s resistance to engine knock. Race fuels often contain additives that elevate knock resistance and decrease thermal sensitivity. When an engine is correctly tuned, this permits the safe use of more aggressive ignition timing or higher boost pressure. A final distinction is superior storage stability in sealed containers, crucial for maintaining consistent performance throughout a race weekend.
Thinking About Running Race Gas In A Normal Car?
Yes, you can put racing fuel in a regular car, but it is rarely beneficial without a tune, and the wrong blend can cause sensor and emissions issues. Get a simple do and do not guide for unleaded vs leaded, oxygenated fuels, and when to avoid it completely.
How Does This Difference Affect Vehicle Performance?
When an engine is specifically tuned for a higher octane fuel, it enables the use of more aggressive timing and higher cylinder pressure without causing destructive knock. This optimization can lead to improved horsepower and offer crucial protection to parts under stress. This is precisely why enthusiasts ask what octane is race fuel and what octane is race gas when planning an engine tune. Without the proper tune, performance gains may be minimal, and drivability could even suffer.
What Octane Ratings Do Race Fuels Use And Why Do They Matter?
Octane rating indicates a fuel’s resistance to premature detonation, commonly known as “knock,” which can severely damage an engine, especially under high-compression or boosted conditions. This critical characteristic explains why inquiries such as what is race fuel octane and what octane is racing fuel are frequently asked. While many racing fuels fall in the 100 to 110+ range, the optimal choice depends on factors like compression ratio, boost pressure, intake air temperature, and ignition timing. Using the lowest octane that effectively prevents knock under the worst expected conditions is the safest and most efficient approach; excessive octane provides no further benefit if the engine doesn’t require it. Here are practical guidelines that help connect octane to use.
- Higher compression and more boost generally require higher race fuel octane rating.
- Hotter ambient conditions can increase knock risk, raising the need for race fuel octane.
- Aggressive ignition timing can demand higher racing fuel octane to stay safe.
- Rulebooks may define the fuel, so what octane is race gas can be fixed by regulation.
- Data logs and knock monitoring are the best way to validate fuel choice.
When someone asks what’s racing fuel is, octane is only one piece. Consistency and burn behavior often matter just as much for reliable tuning.
What Fuel Do Race Cars Use Across Different Motorsports?
The type of fuel used in a race car is determined by the specific racing series’ regulations, the engine’s design, and the desired performance characteristics. Consequently, the term “race car fuel” doesn’t refer to a single product but rather to various fuel types. These include specialty fuels, methanol, ethanol, and gasoline-based blends.
Common examples are listed below;
- Drag racing frequently employs race gasoline or alcohol-based fuels, with the choice often determined by the vehicle’s class and power specifications.
- For drift events, especially those involving turbocharged engines, high-octane race fuel blends are common.
- Stock car series often mandate a specific unleaded race gasoline that all participating teams must purchase.
- Karting fuels can range from spec fuels to standard pump fuel or specialized racing blends, all depending on the governing rules.
- Open-wheel and endurance racing typically rely on tightly regulated fuel blends, which may also incorporate renewable components to comply with current regulations.
The key point is that rules shape the answer to what is racing gas and what fuel do race cars use. Always follow the sanctioning body fuel specification.

Can You Put Racing Gas In A Normal Car And What Happens If You Do?
Many drivers frequently ask, can I put racing fuel in my car, and similar questions like can you put racing fuel in a regular car or can you put race fuel in a normal car. The definitive answer depends on the specific fuel type and the vehicle’s design. If the race fuel is unleaded and the car is mechanically sound, a limited quantity might be used without causing immediate damage. However, it is unlikely to yield performance improvements in a stock engine. This is because the engine control unit, or ECU, is not calibrated to adjust timing or boost to take advantage of the fuel’s enhanced knock resistance. Furthermore, if the fuel is oxygenated, the car’s operation may change, potentially running richer, due to the altered fueling requirements.
There are various potential issues to consider, including compatibility with the vehicle’s emissions control systems, fuel sensors, and oxygen sensors, particularly if the racing fuel contains lead. For these reasons, the safest recommendation is to consistently use the fuel grade for which your vehicle was originally engineered, unless you have a specialized engine tune and a clear justification. If you decide to use race fuel for a specific performance goal, it must be integrated into a carefully matched and calibrated setup. In summary, the answer to can you put racing fuel in a regular car is occasionally yes, but it is seldom beneficial and carries the risk of creating operational problems if the fuel’s chemical composition is not fully compatible with your vehicle’s systems.
What Happens If You Mix Race Gas With Regular Pump Gas?
Fuel mixing is often used to achieve a mid-level or target racing octane for street cars without buying a full tank of race fuel. However, mixing can hurt consistency, and some blends should not be combined. The resulting octane is usually a volume-weighted average, but real-world results vary because fuel blending characteristics differ. Mixing alters volatility and burn behavior, meaning a blended tank may not perform like a single, pre-formulated fuel with the same posted octane. Below are safety and compatibility tips when mixing race gas and regular gas.
- Avoid mixing leaded and unleaded fuels in vehicles with emissions equipment.
- Avoid mixing oxygenated race fuel with unknown pump blends if you cannot tune for it.
- Use clean containers and avoid water, dirt, and old residues in race gas cans.
- If you are chasing a specific race fuel octane rating, test and log rather than guessing.
- If you must mix, mix thoroughly and maintain consistent ratios.
Mixing can be useful, but it is not a substitute for choosing the right fuel and tuning properly.
Mixing Race Gas And Pump Gas To Hit A Target Octane?
Mixing can work, but it can also wreck consistency, volatility, and real world results, even if the posted octane looks right. Use this mixing worksheet to estimate your blend, avoid bad combinations, and follow the safest handling rules for clean containers and repeatable ratios.
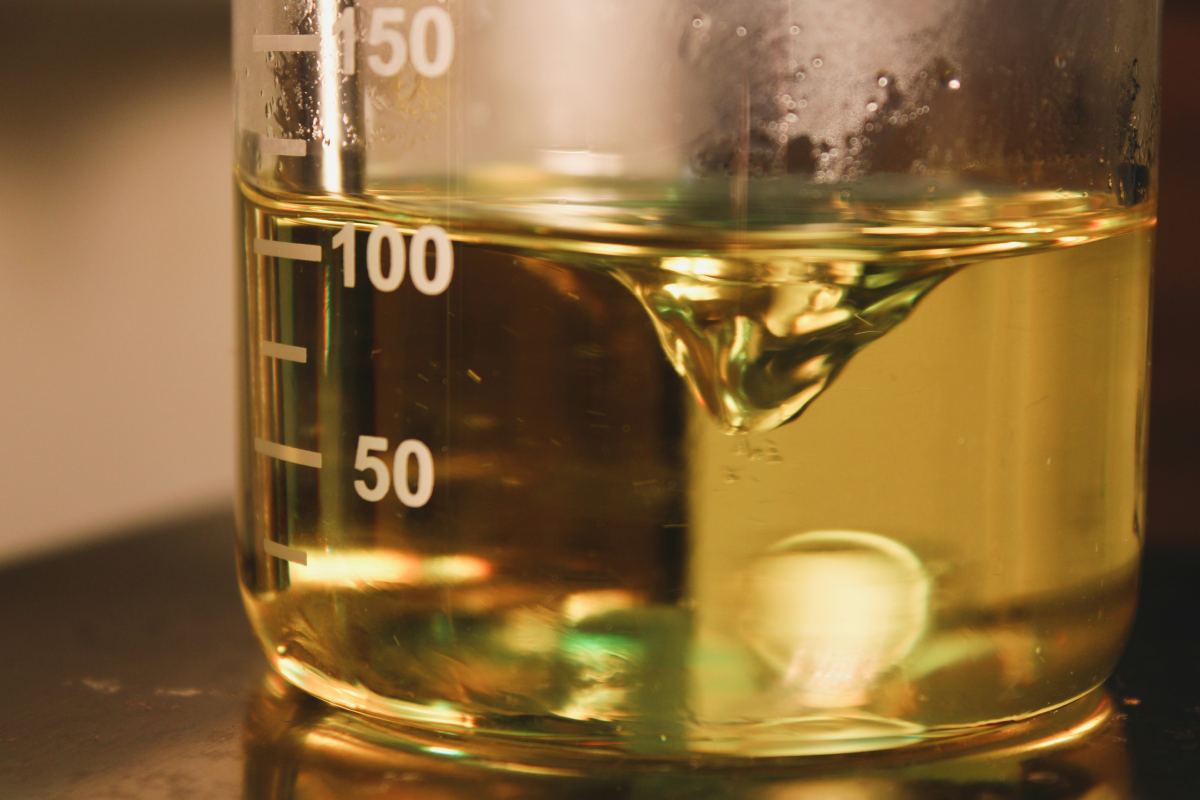
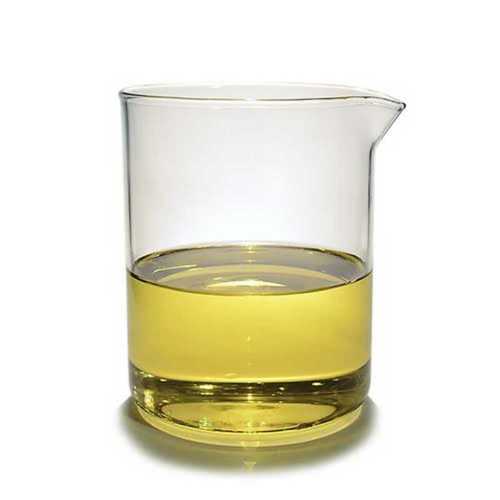
What Does Race Fuel Look Like And How Can You Identify It?
The frequent question about race fuel color arises because many high-performance fuels are intentionally dyed. This practice of using dyes serves multiple purposes, including easy visual identification, adherence to stringent shipping compliance standards, and enabling quick verification checks within a race’s pit area. Different fuel manufacturers or brands commonly employ distinct colors for their various blends. It is important to note that the color itself is not an indicator of the fuel’s octane rating. Instead, it functions as a useful tool to help prevent confusion or mix-ups during a competitive racing event.
You might also encounter the term race car gas when referring to these speciality dyed blends that are distinctly different from standard pump fuel. For accurate identification, however, one must always rely on the official product label, the detailed specification sheet, and the rules published by the relevant sanctioning body. When purchasing fuel for performance applications, the main focus should be on the published chemical properties and sourcing from a trustworthy supplier. Phrases like racing fuel phoenix simply indicate regional availability.